Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) inhibits the cell migration and invasion in human glioma cell lines in vitro
- PMID: 26823735
- PMCID: PMC4713521
Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) inhibits the cell migration and invasion in human glioma cell lines in vitro
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects and the potential mechanisms of RKIP on cell migration, invasion and proliferation in human glioma cell lines in vitro.
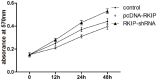
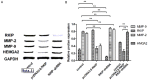
Methods: The RKIP over-expressing and RKIP knockdown human U87 glioma cells were used to reveal the effects of RKIP on human glioma cells migration, invasion and proliferation. After the recombinant plasmid pcDNA3.0-RKIP or RKIP-shRNA was transfected into the cell lines U87 by the means of liposome assay, the cells migration, invasion and proliferation were detected by wound healing, Transwell and MTT assay. Then, the levels of RKIP, MMP-3, MMP-9 and HMGA2 mRNA transcription were measured by means of RT-qPCR and levels of proteins expressions were determined using Western blot.
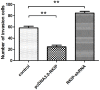
Results: The results of MTT assay suggested that the PKIP have little inhibitive effects on glioma cells proliferation (P>0.05). The present paper showed that the migration distances in the group of RKIP-shRNA were markedly increased compared to the pcDNA3.0-RKIP and control. Similarly, the results showed that the numbers of invasion cells in RKIP-shRNA were remarkably increased than the pcDNA3.0-RKIP group and control group. Western blot and RT-qPCR suggested that over-expressions of RKIP lessened the MMP-2, MMP-9 and HMGA2 expression, however, turning down the RKIP expression showed the inverse effects.
Conclusion: RKIP inhibits the cells migrations and invasions. Meanwhile, RKIP might inhibit the glioma cells through inhibiting MMPs and HMAG2 expression. Therefore, we demonstrated that RKIP is an underlying target for the treatment of glioma.
Keywords: HMGA2; Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP); glioma; invasion; migration.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RKIP inhibits gastric cancer cell survival and invasion by regulating the expression of HMGA2 and OPN.Tumour Biol. 2014 Dec;35(12):11949-58. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2486-8. Epub 2014 Aug 30. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25172097
-
Overexpression of RKIP inhibits cell invasion in glioma cell lines through upregulation of miR-98.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:695179. doi: 10.1155/2013/695179. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24392454 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship between raf kinase inhibitor protein and metastasis of ovarian carcinoma].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2009 Jul;44(7):522-8. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19957553 Chinese.
-
Overexpression of RKIP and its cross-talk with several regulatory gene products in multiple myeloma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 May 5;36(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0535-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28476134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Linkage between the Tumor Suppressor RKIP and Autophagy: Targeted Therapeutics.Crit Rev Oncog. 2018;23(5-6):281-305. doi: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2018027211. Crit Rev Oncog. 2018. PMID: 30311561 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of Annexin-A1 Inhibits Growth, Migration and Invasion of Glioma Cells by Suppressing the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway.ASN Neuro. 2021 Jan-Dec;13:17590914211001218. doi: 10.1177/17590914211001218. ASN Neuro. 2021. PMID: 33706561 Free PMC article.
-
The Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type-2(TRPV2) Ion Channels in Neurogenesis andGliomagenesis: Cross-Talk between TranscriptionFactors and Signaling Molecules.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Mar 6;11(3):322. doi: 10.3390/cancers11030322. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30845786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanical and pharmacological regulation of glioblastoma cell migration in 3D matrices.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Apr;234(4):3948-3960. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27209. Epub 2018 Aug 21. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30132879 Free PMC article.
-
RKIP: A Key Regulator in Tumor Metastasis Initiation and Resistance to Apoptosis: Therapeutic Targeting and Impact.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Aug 24;10(9):287. doi: 10.3390/cancers10090287. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30149591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Stochastic Binary Model for the Regulation of Gene Expression to Investigate Responses to Gene Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 27;14(3):633. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030633. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams DA, Hanson JA, Brown JM, Hsu FP, Delashaw JB Jr, Bota DA. Timing of surgery and bevacizumab therapy in neurosurgical patients with recurrent high grade glioma. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Afshordel S, Kern B, Clasohm J, Konig H, Priester M, Weissenberger J, Kogel D, Eckert GP. Lovastatin and perillyl alcohol inhibit glioma cell invasion, migration, and proliferation--impact of Ras-/Rho-prenylation. Pharmacol Res. 2015;91:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Yang L, Gao S, Asghar S, Liu G, Song J, Wang X, Ping Q, Zhang C, Xiao Y. Hyaluronic acid/chitosan nanoparticles for delivery of curcuminoid and its in vitro evaluation in glioma cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;72:1391–1401. - PubMed
-
- Escara-Wilke J, Keller JM, Ignatoski KM, Dai J, Shelley G, Mizokami A, Zhang J, Yeung ML, Yeung KC, Keller ET. Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) deficiency decreases latency of tumorigenesis and increases metastasis in a murine genetic model of prostate cancer. Prostate. 2015;75:292–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
