Roles of Cx43 and AKAP95 in ovarian cancer tissues in G1/S phase
- PMID: 26823747
- PMCID: PMC4713533
Roles of Cx43 and AKAP95 in ovarian cancer tissues in G1/S phase
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression of A-kinase anchor protein 95 (AKAP95), cell cycle protein E1 (cyclinE1) and D1 (cyclinD1), and gap junction protein connexin 43 (Cx43) in ovarian cancer tissues, the relationship between four proteins and clinicopathologic parameters, and the correlation between these proteins.
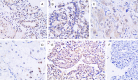
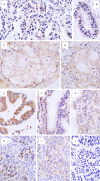
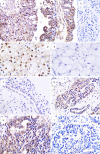
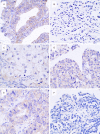
Methods: The expression of proteins in 54 cases of ovarian cancer tissues was detected by immunohistochemical method.
Results: The positive expression rates of AKAP95, cyclinD1 and cyclinE1 in ovarian cancer tissues were 72.22%, 66.67% and 79.63%, respectively, which were higher than that of ovarian pericarcinoma tissues expressing as 33.33%, 25% and 8.30% (P<0.05). The positive expression rate of Cx43 in ovarian cancer tissues was 40.74%, which was lower than that of ovarian pericarcinoma tissues expressing as 75%; respectively, and the difference was statistically significant between groups (P<0.05). The expression of cyclinD1 in ovarian cancer tissues was related to the histologic type (P<0.05) while it showed no correlation with the degree of differentiation (P>0.05). Additionally, the expression of AKAP95, Cx43 and cyclinE1 in ovarian cancer tissues showed no correlation with the degree of differentiation or the histologic type (P>0.05). Protein expressions of AKAP95, Cx43 and cyclinE1 were correlated with each other (P<0.05), and the expressions of cyclinD1, cyclinE1 and Cx43 were also correlated with each other (P<0.05). However, AKAP95 and cyclinD1 showed no correlation (P>0.05).
Conclusion: AKAP95, cyclinD1 and cyclinE1 play an important role in promoting the process of ovarian cancer formation. The tumor inhibitory effects of Cx43 protein on the pathogenesis of ovarian cancer were weakened. The expression of cyclinD1 in ovarian cancer tissues is related to the histologic type while it shows no correlation with the degree of differentiation. Additionally, the expression of AKAP95, Cx43 and cyclinE1 in ovarian cancer tissues shows no correlation with the degree of differentiation or the histologic type. AKAP95 expression is correlated with Cx43 and cyclinE1 expression; Cx43 expression is correlated with AKAP95, cyclinD1 and cyclinE1 expression; cyclinE1 expression is correlated with AKAP95, Cx43, cyclinD1 expression; cyclinD1 expression is correlated with Cx43 and cyclinE1 expression, while AKAP95 and cyclinD1 show no correlation.
Keywords: AKAP95; Cx43; correlation; cyclinD1; cyclinE1; ovarian cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Musgrove EA, Caldon CE, Barraclough J, Stone A, Sutherland RL. CyclinD as a therapeutic target in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:558–572. - PubMed
-
- Koff A, Giordano A, Desai D, Yamashita K, Harper JW, Elledge S, Nishimoto T, Morgan DO, Franza BR, Roberts JM. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992;257:1689–1694. - PubMed
-
- Arsenijevic T, Degraef C, Dumont JE, Roger PP, PirsonI I. G1/S Cyclins interact with regulatory subunit of PKA via A-kinase anchoring protein, AKAP95. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:1217–1222. - PubMed
-
- Zhang YW, Nakayama K, Nakayama K, Morita I. A novel route for Connexin 43 to inhibit cell proliferation: negative regulation of S-phase kinase-associated protein (skp2) Cancer Res. 2003;63:1623–1630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
