MiR-145 suppressed human retinoblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting ADAM19
- PMID: 26823772
- PMCID: PMC4713558
MiR-145 suppressed human retinoblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting ADAM19
Abstract
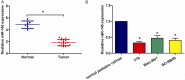
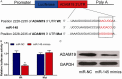
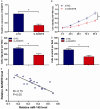
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play critical roles in retinoblastoma (RB) initiation and progression, aberrant expression of miR-145 had been frequently reported in cancer studies. However, the role and mechanism of its function in RB is still unclear. In this study, our data showed that miR-145 was downregulated in RB tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of miR-145 suppressed RB cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. ADAM19 was identified as a direct target of miR-145. Silencing of ADAM19 significantly inhibited RB cell proliferation, migration and invasion. In addition, a reverse correlation between miR-145 and ADAM19 expression was noted in RB tissues. Taken together, these findings suggested that miR-145 functions as a tumor suppressor in RB by directly targeting ADAM19. miR-145 could be an anticancer therapeutic target for RB patients.
Keywords: ADAM19; Retinoblastoma; miR-145.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circular RNA has_circ_0000034 accelerates retinoblastoma advancement through the miR-361-3p/ADAM19 axis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Jan;476(1):69-80. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03886-5. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 32844346
-
MiR-613 suppresses retinoblastoma cell proliferation, invasion, and tumor formation by targeting E2F5.Tumour Biol. 2017 Mar;39(3):1010428317691674. doi: 10.1177/1010428317691674. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28351331
-
MiR-142-5p promotes retinoblastoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting PTEN.J Biochem. 2021 Oct 11;170(2):195-202. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvaa121. J Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34562091
-
Mechanism and function of miR-140 in human cancers: A review and in silico study.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Jan;241:154265. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154265. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 36509008 Review.
-
Emerging Role of Circular RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Retinoblastoma.Ophthalmic Res. 2024;67(1):51-61. doi: 10.1159/000535329. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Ophthalmic Res. 2024. PMID: 38109867 Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-145: a potential biomarker of cancer migration and invasion.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Nov 15;11(11):6739-6753. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31814885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of non-coding RNAs and exosomal non-coding RNAs in retinoblastoma progression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 23;10:1065837. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1065837. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36619866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA‑98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k‑Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.Int J Oncol. 2019 Mar;54(3):807-820. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4689. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30664191 Free PMC article.
-
ADAM10 and ADAM17-Novel Players in Retinoblastoma Carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 20;23(20):12621. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012621. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293469 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers in retinoblastoma.Int J Ophthalmol. 2020 Feb 18;13(2):325-341. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2020.02.18. eCollection 2020. Int J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32090044 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Dimaras H, Kimani K, Dimba EA, Gronsdahl P, White A, Chan HS, Gallie BL. Retinoblastoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1436–1446. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:597–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
