Influence of protein kinase C (PKC) on the prognosis of diabetic nephropathy patients
- PMID: 26823823
- PMCID: PMC4713609
Influence of protein kinase C (PKC) on the prognosis of diabetic nephropathy patients
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the association between protein kinase C (PKC) and the prognosis of patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN).
Methods: 92 patients with DN who had received treatments with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) or angiotensin-receptor blockade (ARB) were collected. The clinicopathologic characteristics were recorded and a 4-year follow-up with the final result of impaired renal functions (eGFR < 40 mL/min) was conducted. The expression of PKC was detected by immunohistochemical assay. Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analysis were performed to estimate the effects of PKC on DN prognosis.
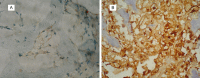
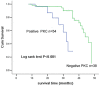
Results: According to immunohistochemical analysis, there were 54 cases with positive expression of PKC (positive rate 58.7%). Meanwhile, during the follow-up, the urine protein, mean serum creatinine and eGFR in patients with positive PKC were all higher than those in negative expression group (P < 0.05). The expression of PKC was influenced by age (P < 0.001), course of disease (P < 0.001), blood pressure (P = 0.002), blood glucose (P < 0.001), HbA1c (P = 0.002), renal functions of patients before (P = 0.011) and after (P = 0.041) the biopsy. Besides, the Kaplan-Meier curve revealed that patients with positive PKC expression had shorter survival time than those with negative PKC expression (P < 0.001). Cox regression analysis indicated that HbA1c (P = 0.009), renal functions of patients after the biopsy (P = 0.002) and PKC (P = 0.028) were important factors in the prognosis of DN and they might be independent prognostic markers.
Conclusion: The expression of PKC is relatively higher in DN patients than in healthy controls. And PKC may be a valuable prognostic marker for patients with DN.
Keywords: PKC; diabetic nephropathy; prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Protein kinase C-betaI, betaII in mouse diabetic nephropathy kidney and its relation to nephroprotective actions of the angiotensin receptor blocker telmisartan].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Jul 24;87(28):1991-5. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17923043 Chinese.
-
Association between physiological serum total bilirubin concentrations and the progression of diabetic nephropathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 May 29;16:1588568. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1588568. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40510475 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of PKC-MAPK pathway mRNAs correlates with glomerular lesions in human diabetic nephropathy.Kidney Int. 2004 Sep;66(3):1107-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00798.x. Kidney Int. 2004. PMID: 15327405
-
Protein kinase C beta inhibitors: a new therapeutic target for diabetic nephropathy and vascular complications.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;22(3):231-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00583.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18485142 Review.
-
Lessons learned from studies of the natural history of diabetic nephropathy in young type 1 diabetic patients.Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008 Aug;5 Suppl 4:958-63. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18806710 Review.
Cited by
-
Serotonin and Its Receptor as a New Antioxidant Therapeutic Target for Diabetic Kidney Disease.J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:7680576. doi: 10.1155/2017/7680576. Epub 2017 Aug 8. J Diabetes Res. 2017. PMID: 28929122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Approach Based on Metabolomics Coupled With Intestinal Flora Analysis and Network Pharmacology to Explain the Mechanisms of Action of Bekhogainsam Decoction in the Improvement of Symptoms of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 21;11:633. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00633. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32508632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng DP, Placha G, Choo S, Chia KS, Warram JH, Krolewski AS. A disease haplotype for advanced nephropathy in type 2 diabetes at the ACE locus. Diabetes. 2006;55:2660–2663. - PubMed
-
- Santi D, Giannetta E, Isidori AM, Vitale C, Aversa A, Simoni M. Therapy of endocrine disease. Effects of chronic use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on endothelial markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015;172:R103–114. - PubMed
-
- Wolf G. New insights into the pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy: from haemodynamics to molecular pathology. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004;34:785–796. - PubMed
-
- Tang W, Zhou TB, Jiang Z. RETRACTED: Association of the angiotensinogen M235T gene polymorphism with risk of diabetes mellitus developing into diabetic nephropathy. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015;16:NP27–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
