Strain Echocardiography in Acute Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 26823931
- PMCID: PMC4729419
- DOI: 10.5811/westjem.2015.12.28521
Strain Echocardiography in Acute Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
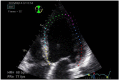
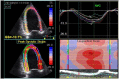
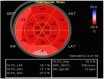
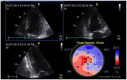
Echocardiography has become a critical tool in the evaluation of patients presenting to the emergency department (ED) with acute cardiovascular diseases and undifferentiated cardiopulmonary symptoms. New technological advances allow clinicians to accurately measure left ventricular (LV) strain, a superior marker of LV systolic function compared to traditional measures such as ejection fraction, but most emergency physicians (EPs) are unfamiliar with this method of echocardiographic assessment. This article discusses the application of LV longitudinal strain in the ED and reviews how it has been used in various disease states including acute heart failure, acute coronary syndromes (ACS) and pulmonary embolism. It is important for EPs to understand the utility of technological and software advances in ultrasound and how new methods can build on traditional two-dimensional and Doppler techniques of standard echocardiography. The next step in competency development for EP-performed focused echocardiography is to adopt novel approaches such as strain using speckle-tracking software in the management of patients with acute cardiovascular disease. With the advent of speckle tracking, strain image acquisition and interpretation has become semi-automated making it something that could be routinely added to the sonographic evaluation of patients presenting to the ED with cardiovascular disease. Once strain imaging is adopted by skilled EPs, focused echocardiography can be expanded and more direct, phenotype-driven care may be achievable for ED patients with a variety of conditions including heart failure, ACS and shock.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Two-dimensional longitudinal strain for the assessment of the left ventricular systolic function as compared with conventional echocardiographic methods in patients with acute coronary syndromes.Kardiol Pol. 2011;69(4):357-62. Kardiol Pol. 2011. PMID: 21523670
-
Early assessment of strain echocardiography can accurately exclude significant coronary artery stenosis in suspected non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014 May;27(5):512-9. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2014.01.019. Epub 2014 Mar 5. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014. PMID: 24612899 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography for quantitative assessment of global left ventricular function: a comparative study to three-dimensional echocardiography.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014 Mar;27(3):285-91. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Dec 8. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014. PMID: 24325960
-
European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging/Cardiovascular Imaging Department of the Brazilian Society of Cardiology recommendations for the use of cardiac imaging to assess and follow patients after heart transplantation.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Sep;16(9):919-48. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jev139. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26139361 Review.
-
Is Speckle Tracking Imaging Ready for Prime Time in Current Echo Clinical Practice?Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2018 Nov-Dec;61(5-6):437-445. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 30408468 Review.
Cited by
-
The value of 2D speckle-tracking strain echocardiography in evaluating the relationship between carotid elasticity and left ventricular systolic function in patients with diabetic nephropathy.Insights Imaging. 2020 Aug 17;11(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13244-020-00897-0. Insights Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32804263 Free PMC article.
-
Global longitudinal strain changes during hemorrhagic shock: An experimental study.Turk J Emerg Med. 2020 Jul 18;20(3):97-104. doi: 10.4103/2452-2473.290066. eCollection 2020 Jul-Sep. Turk J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32832728 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic Techniques of Deformation Imaging in the Evaluation of Maternal Cardiovascular System in Patients with Complicated Pregnancies.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4139635. doi: 10.1155/2017/4139635. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28904957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of cardiac function in children after percutaneous closure of atrial septal defect using speckle tracking echocardiography.ARYA Atheroscler. 2020 Nov;16(6):290-294. doi: 10.22122/arya.v16i6.2128. ARYA Atheroscler. 2020. PMID: 34122583 Free PMC article.
-
Bedside Ultrasound for Hemodynamic Monitoring in Cardiac Intensive Care Unit.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 19;11(24):7538. doi: 10.3390/jcm11247538. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36556154 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Murphy SL, Xu J, Kochanek KD. Deaths: final data for 2010. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2013;61(4):1–117. - PubMed
-
- Labovitz AJ, Noble VE, Bierig M, et al. Focused cardiac ultrasound in the emergent setting: a consensus statement of the American Society of Echocardiography and American College of Emergency Physicians. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010;23(12):1225–30. - PubMed
-
- Matulevicius SA, Rohatgi A, Das SR, et al. Appropriate use and clinical impact of transthoracic echocardiography. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(17):1600–7. - PubMed
-
- Russell FM, Ehrman RR, Cosby K, et al. Diagnosing acute heart failure in patients with undifferentiated dyspnea: a lung and cardiac ultrasound (LuCUS) protocol. Acad Emerg Med. 2015;22(2):182–91. 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

