Species-level resolution of 16S rRNA gene amplicons sequenced through the MinION™ portable nanopore sequencer
- PMID: 26823973
- PMCID: PMC4730766
- DOI: 10.1186/s13742-016-0111-z
Species-level resolution of 16S rRNA gene amplicons sequenced through the MinION™ portable nanopore sequencer
Abstract
Background: The miniaturised and portable DNA sequencer MinION™ has been released to the scientific community within the framework of an early access programme to evaluate its application for a wide variety of genetic approaches. This technology has demonstrated great potential, especially in genome-wide analyses. In this study, we tested the ability of the MinION™ system to perform amplicon sequencing in order to design new approaches to study microbial diversity using nearly full-length 16S rDNA sequences.
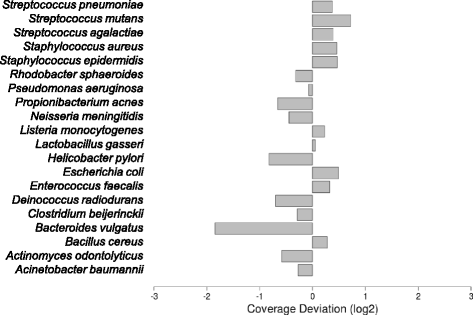
Results: Using R7.3 chemistry, we generated more than 3.8 million events (nt) during a single sequencing run. These data were sufficient to reconstruct more than 90 % of the 16S rRNA gene sequences for 20 different species present in a mock reference community. After read mapping and 16S rRNA gene assembly, consensus sequences and 2d reads were recovered to assign taxonomic classification down to the species level. Additionally, we were able to measure the relative abundance of all the species present in a mock community and detected a biased species distribution originating from the PCR reaction using 'universal' primers.
Conclusions: Although nanopore-based sequencing produces reads with lower per-base accuracy compared with other platforms, the MinION™ DNA sequencer is valuable for both high taxonomic resolution and microbial diversity analysis. Improvements in nanopore chemistry, such as minimising base-calling errors and the nucleotide bias reported here for 16S amplicon sequencing, will further deliver more reliable information that is useful for the specific detection of microbial species and strains in complex ecosystems.
Keywords: 16S rDNA amplicon sequencing; Long-read sequencing; Microbial diversity; MinION; Nanopore sequencer.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

