Up-regulation of immunomodulatory effects of mouse bone-marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells by tetrahydrocannabinol pre-treatment involving cannabinoid receptor CB2
- PMID: 26824325
- PMCID: PMC4872725
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7042
Up-regulation of immunomodulatory effects of mouse bone-marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells by tetrahydrocannabinol pre-treatment involving cannabinoid receptor CB2
Abstract
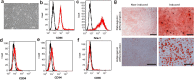
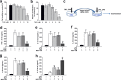
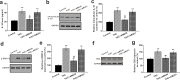
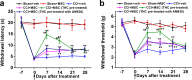
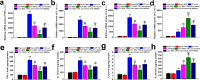
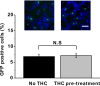
Chronic pain is commonly and closely correlated with inflammation. Both cannabinoid signaling and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been demonstrated to reduce inflammatory pain. Although cannabinoid signaling is essential for mesenchymal stem cell survival and differentiation, little is known about its role in modulatory effect of MSCs on inflammation and pain sensitivity. Here we showed that mouse bone-marrow derived MSCs (BM-MSCs) expressed both cannabinoid receptor type 1 and 2 (CB1 and CB2). CB2 expression level in BM-MSCs increased with their maturation. In addition, we found that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) activated CB2 receptor and ERK signaling, consequently enhancing the modulation of MSCs on inflammation-associated cytokine release from lipopolysaccharides-stimulated microglia. Consistent with in vitro data, THC pretreatment enhanced the immunomodulatory effects of BM-MSC on thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in chronic constriction injury model, by decreasing the release of pro-inflammation cytokines. Our study revealed the crucial role of THC in promoting the immunomodulatory effects of MSCs and proposed a new strategy to alleviate pain based on stem cells therapy.
Keywords: Immune response; Immunity; Immunology and Microbiology Section; cannabinoid receptor; inflammation; mesenchymal stem cells; pain; tetrahydrocannabinol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic cannabinoid receptor 2 activation reverses paclitaxel neuropathy without tolerance or cannabinoid receptor 1-dependent withdrawal.Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Mar 1;77(5):475-87. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.04.009. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 24853387 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 and their cognate cannabinoid ligands in murine embryonic stem cells.PLoS One. 2007 Jul 25;2(7):e641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000641. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17653268 Free PMC article.
-
The cannabinoid delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol inhibits RAS-MAPK and PI3K-AKT survival signalling and induces BAD-mediated apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells.Int J Cancer. 2007 Nov 15;121(10):2172-80. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22917. Int J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17583570
-
Targeting the endocannabinoid system with cannabinoid receptor agonists: pharmacological strategies and therapeutic possibilities.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Dec 5;367(1607):3353-63. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0381. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23108552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor as a Potential Target in Myocardial Infarction: Exploration of Molecular Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 30;25(3):1683. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031683. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pretreatment with AM1241 Enhances the Analgesic Effect of Intrathecally Administrated Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Sep 10;2019:7025473. doi: 10.1155/2019/7025473. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 31611918 Free PMC article.
-
2-Arachidonoylglycerol Modulates CXCL12-Mediated Chemotaxis in Mantle Cell Lymphoma and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;15(5):1585. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051585. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900374 Free PMC article.
-
Boosting brain glucose metabolism to fight neurodegeneration?Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 28;8(9):14273-14274. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15131. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28184023 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells in combination with erythropoietin repair hyperoxia-induced alveoli dysplasia injury in neonatal mice via inhibition of TGF-β1 signaling.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):47082-47094. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9314. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27191651 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the antinociceptive and reparative actions of mesenchymal stem cells in rats with peripheral neuropathic pain.Ibrain. 2023 Aug 24;9(3):245-257. doi: 10.1002/ibra.12129. eCollection 2023 Fall. Ibrain. 2023. PMID: 37786759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Staud R, Koo EB. Are cannabinoids a new treatment option for pain in patients with fibromyalgia? Nature clinical practice Rheumatology. 2008;4:348–349. - PubMed
-
- Karst M, Wippermann S. Cannabinoids against pain. Efficacy and strategies to reduce psychoactivity: a clinical perspective. Expert opinion on investigational drugs. 2009;18:125–133. - PubMed
-
- Attal N, Brasseur L, Guirimand D, Clermond-Gnamien S, Atlami S, Bouhassira D. Are oral cannabinoids safe and effective in refractory neuropathic pain? European journal of pain. 2004;8:173–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

