Phosphoproteomics reveals that Parkinson's disease kinase LRRK2 regulates a subset of Rab GTPases
- PMID: 26824392
- PMCID: PMC4769169
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.12813
Phosphoproteomics reveals that Parkinson's disease kinase LRRK2 regulates a subset of Rab GTPases
Abstract
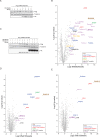
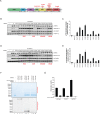
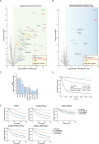
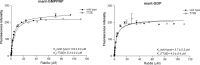
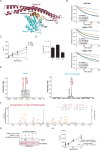
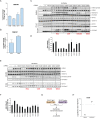
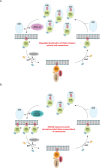
Mutations in Park8, encoding for the multidomain Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein, comprise the predominant genetic cause of Parkinson's disease (PD). G2019S, the most common amino acid substitution activates the kinase two- to threefold. This has motivated the development of LRRK2 kinase inhibitors; however, poor consensus on physiological LRRK2 substrates has hampered clinical development of such therapeutics. We employ a combination of phosphoproteomics, genetics, and pharmacology to unambiguously identify a subset of Rab GTPases as key LRRK2 substrates. LRRK2 directly phosphorylates these both in vivo and in vitro on an evolutionary conserved residue in the switch II domain. Pathogenic LRRK2 variants mapping to different functional domains increase phosphorylation of Rabs and this strongly decreases their affinity to regulatory proteins including Rab GDP dissociation inhibitors (GDIs). Our findings uncover a key class of bona-fide LRRK2 substrates and a novel regulatory mechanism of Rabs that connects them to PD.
Keywords: LRRK2; biochemistry; cell biology; chemical proteomics; human; mouse; neurodegeneration; parkinson-s disease; phosphoproteomics; rabs.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
SWi: Employee of GlaxoSmithKline, a global healthcare company that may conceivably benefit financially through this publication.
MJF: Employee of Merck Research Laboratories.
JAM: Employee of GlaxoSmithKline, a global healthcare company that may conceivably benefit financially through this publication.
ADR: Employee of Merck Research Laboratories, Contributed unpublished essential data or reagents.
Figures
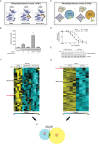
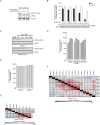
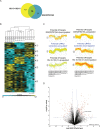
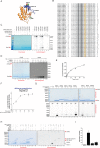
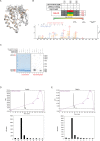
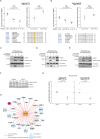
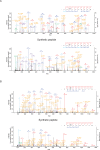
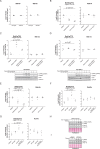

Comment in
-
Parkinson's Disease: A Traffic Jam?Curr Biol. 2016 Apr 25;26(8):R332-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.03.001. Curr Biol. 2016. PMID: 27115692
-
Identification of bona-fide LRRK2 kinase substrates.Mov Disord. 2016 Aug;31(8):1140-1. doi: 10.1002/mds.26647. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Mov Disord. 2016. PMID: 27126091 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baptista MAS, Dave KD, Frasier MA, Sherer TB, Greeley M, Beck MJ, Varsho JS, Parker GA, Moore C, Churchill MJ, Meshul CK, Fiske BK. Loss of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) in rats leads to progressive abnormal phenotypes in peripheral organs. PLoS One. 2013;8:e12813. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080705. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

