Determination of B-Cell Epitopes in Patients with Celiac Disease: Peptide Microarrays
- PMID: 26824466
- PMCID: PMC4732949
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147777
Determination of B-Cell Epitopes in Patients with Celiac Disease: Peptide Microarrays
Abstract
Background: Most antibodies recognize conformational or discontinuous epitopes that have a specific 3-dimensional shape; however, determination of discontinuous B-cell epitopes is a major challenge in bioscience. Moreover, the current methods for identifying peptide epitopes often involve laborious, high-cost peptide screening programs. Here, we present a novel microarray method for identifying discontinuous B-cell epitopes in celiac disease (CD) by using a silicon-based peptide array and computational methods.
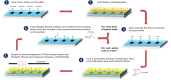
Methods: Using a novel silicon-based microarray platform with a multi-pillar chip, overlapping 12-mer peptide sequences of all native and deamidated gliadins, which are known to trigger CD, were synthesized in situ and used to identify peptide epitopes.
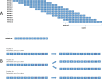
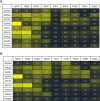
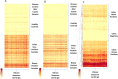
Results: Using a computational algorithm that considered disease specificity of peptide sequences, 2 distinct epitope sets were identified. Further, by combining the most discriminative 3-mer gliadin sequences with randomly interpolated3- or 6-mer peptide sequences, novel discontinuous epitopes were identified and further optimized to maximize disease discrimination. The final discontinuous epitope sets were tested in a confirmatory cohort of CD patients and controls, yielding 99% sensitivity and 100% specificity.
Conclusions: These novel sets of epitopes derived from gliadin have a high degree of accuracy in differentiating CD from controls, compared with standard serologic tests. The method of ultra-high-density peptide microarray described here would be broadly useful to develop high-fidelity diagnostic tests and explore pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Deamidated gliadin peptides form epitopes that transglutaminase antibodies recognize.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008 Mar;46(3):253-61. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31815ee555. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18376241
-
In vivo antigen challenge in celiac disease identifies a single transglutaminase-modified peptide as the dominant A-gliadin T-cell epitope.Nat Med. 2000 Mar;6(3):337-42. doi: 10.1038/73200. Nat Med. 2000. PMID: 10700238
-
Detection of specific IgA antibodies against a novel deamidated 8-Mer gliadin peptide in blood plasma samples from celiac patients.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 22;8(11):e80982. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080982. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278359 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen presentation to celiac lesion-derived T cells of a 33-mer gliadin peptide naturally formed by gastrointestinal digestion.J Immunol. 2004 Aug 1;173(3):1757-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.3.1757. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15265905
-
[The identification of the immunodominant gliadin epitope].Harefuah. 2003 Jul;142(7):554-7, 564. Harefuah. 2003. PMID: 12908394 Review. Hebrew.
Cited by
-
Coeliac disease: a unique model for investigating broken tolerance in autoimmunity.Clin Transl Immunology. 2016 Nov 2;5(11):e112. doi: 10.1038/cti.2016.58. eCollection 2016 Nov. Clin Transl Immunology. 2016. PMID: 27990287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An ultra-high-density protein microarray for high throughput single-tier serological detection of Lyme disease.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 22;10(1):18085. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75036-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33093502 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-gliadin specific celiac disease antibodies recognize p31-43 and p57-68 alpha gliadin peptides in deamidation related manner as a result of cross-reaction.Amino Acids. 2021 Jul;53(7):1051-1063. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03006-7. Epub 2021 May 31. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 34059947 Free PMC article.
-
High Frequency of Extractable Nuclear Autoantibodies in Wheat-Related Disorders.Biomark Insights. 2018 Jun 18;13:1177271918782893. doi: 10.1177/1177271918782893. eCollection 2018. Biomark Insights. 2018. PMID: 29977112 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Vibrant DNA microarray for the high-throughput multiplex detection of enteric pathogens in clinical samples.Gut Pathog. 2019 Oct 18;11:51. doi: 10.1186/s13099-019-0329-2. eCollection 2019. Gut Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31636718 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

