Electron Transport Chain Remodeling by GSK3 during Oogenesis Connects Nutrient State to Reproduction
- PMID: 26824655
- PMCID: PMC6894174
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.020
Electron Transport Chain Remodeling by GSK3 during Oogenesis Connects Nutrient State to Reproduction
Abstract
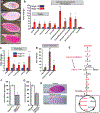
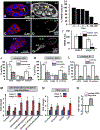
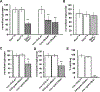
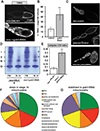
Reproduction is heavily influenced by nutrition and metabolic state. Many common reproductive disorders in humans are associated with diabetes and metabolic syndrome. We characterized the metabolic mechanisms that support oogenesis and found that mitochondria in mature Drosophila oocytes enter a low-activity state of respiratory quiescence by remodeling the electron transport chain (ETC). This shift in mitochondrial function leads to extensive glycogen accumulation late in oogenesis and is required for the developmental competence of the oocyte. Decreased insulin signaling initiates ETC remodeling and mitochondrial respiratory quiescence through glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3). Intriguingly, we observed similar ETC remodeling and glycogen uptake in maturing Xenopus oocytes, suggesting that these processes are evolutionarily conserved aspects of oocyte development. Our studies reveal an important link between metabolism and oocyte maturation.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Acevedo N, Ding J, and Smith GD (2007). Insulin signaling in mouse oocytes. Biol Reprod 77, 872–879. - PubMed
-
- Arden KC (2004). FoxO: linking new signaling pathways. Mol Cell 14, 416–418. - PubMed
-
- Barri PN, Coroleu B, Clua E, Tur R, Boada M, and Rodriguez I (2014). Investigations into implantation failure in oocyte-donation recipients. Reprod Biomed Online 28, 99–105. - PubMed
-
- Barthel A, Schmoll D, and Unterman TG (2005). FoxO proteins in insulin action and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 16, 183–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

