Core promoter-specific gene regulation: TATA box selectivity and Initiator-dependent bi-directionality of serum response factor-activated transcription
- PMID: 26824723
- PMCID: PMC4818687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.01.005
Core promoter-specific gene regulation: TATA box selectivity and Initiator-dependent bi-directionality of serum response factor-activated transcription
Abstract
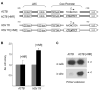
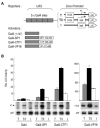
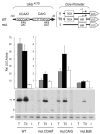
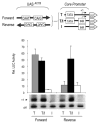
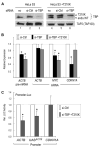
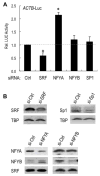
Gene-specific activation by enhancers involves their communication with the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery at the core promoter. Core promoters are diverse and may contain a variety of sequence elements such as the TATA box, the Initiator (INR), and the downstream promoter element (DPE) recognized, respectively, by the TATA-binding protein (TBP) and TBP-associated factors of the TFIID complex. Core promoter elements contribute to the gene selectivity of enhancers, and INR/DPE-specific enhancers and activators have been identified. Here, we identify a TATA box-selective activating sequence upstream of the human β-actin (ACTB) gene that mediates serum response factor (SRF)-induced transcription from TATA-dependent but not INR-dependent promoters and requires the TATA-binding/bending activity of TBP, which is otherwise dispensable for transcription from a TATA-less promoter. The SRF-dependent ACTB sequence is stereospecific on TATA promoters but activates in an orientation-independent manner a composite TATA/INR-containing promoter. More generally, we show that SRF-regulated genes of the actin/cytoskeleton/contractile family tend to have a TATA box. These results suggest distinct TATA-dependent and INR-dependent mechanisms of TFIID-mediated transcription in mammalian cells that are compatible with only certain stereospecific combinations of activators, and that a TBP-TATA binding mechanism is important for SRF activation of the actin/cytoskeleton-related gene family.
Keywords: Core promoter-selective transcription activation; Gene regulation; RNA polymerase II; TATA box; TATA-binding protein.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SAGA mediates transcription from the TATA-like element independently of Taf1p/TFIID but dependent on core promoter structures in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 27;12(11):e0188435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188435. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29176831 Free PMC article.
-
Taspase1 processing alters TFIIA cofactor properties in the regulation of TFIID.Transcription. 2015;6(2):21-32. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2015.1052178. Transcription. 2015. PMID: 25996597 Free PMC article.
-
A transcription factor IIA-binding site differentially regulates RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription in a promoter context-dependent manner.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 14;292(28):11873-11885. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.770412. Epub 2017 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28539359 Free PMC article.
-
TRF2: TRansForming the view of general transcription factors.Transcription. 2015;6(1):1-6. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2015.1004980. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Transcription. 2015. PMID: 25588059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the TATA-box binding protein (TBP) and associated family members in transcription regulation.Gene. 2022 Jul 30;833:146581. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146581. Epub 2022 May 18. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35597524 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational identification of eukaryotic promoters based on cascaded deep capsule neural networks.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jul 20;22(4):bbaa299. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa299. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33227813 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Enhancer-Mediated Transcriptional Regulation in Precision Biology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 29;24(13):10843. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310843. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding regulatory elements: Potential roles in disease and the case of epilepsy.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2022 Apr;48(3):e12775. doi: 10.1111/nan.12775. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 34820881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Analysis of Two Zinc (Zn) Transporters (ZIP3 and ZIP8) Promoters and Their Distinct Response to MTF1 and RREB1 in the Regulation of Zn Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 26;21(17):6135. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176135. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32858813 Free PMC article.
-
Second heart field-specific expression of Nkx2-5 requires promoter proximal interaction with Srf.Mech Dev. 2020 Jun;162:103615. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2020.103615. Epub 2020 May 22. Mech Dev. 2020. PMID: 32450132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roeder RG. The role of general initiation factors in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21:327–335. - PubMed
-
- Roeder RG. Transcriptional regulation and the role of diverse coactivators in animal cells. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:909–915. - PubMed
-
- Smale ST, Kadonaga JT. The RNA polymerase II core promoter. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:449–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

