Evaluation of the C-Terminal Fragment of Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc Lectin Intermediate Subunit as a Vaccine Candidate against Amebic Liver Abscess
- PMID: 26824828
- PMCID: PMC4732598
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004419
Evaluation of the C-Terminal Fragment of Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc Lectin Intermediate Subunit as a Vaccine Candidate against Amebic Liver Abscess
Abstract
Background: Entamoeba histolytica is an intestinal protozoan parasite that causes amoebiasis, including amebic dysentery and liver abscesses. E. histolytica invades host tissues by adhering onto cells and phagocytosing them depending on the adaptation and expression of pathogenic factors, including Gal/GalNAc lectin. We have previously reported that E. histolytica possesses multiple CXXC sequence motifs, with the intermediate subunit of Gal/GalNAc lectin (i.e., Igl) as a key factor affecting the amoeba's pathogenicity. The present work showed the effect of immunization with recombinant Igl on amebic liver abscess formation and the corresponding immunological properties.
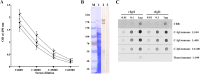
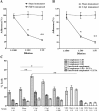
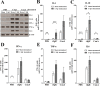
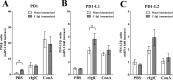
Methodology/principal findings: A prokaryotic expression system was used to prepare the full-length Igl and the N-terminal, middle, and C-terminal fragments (C-Igl) of Igl. Vaccine efficacy was assessed by challenging hamsters with an intrahepatic injection of E. histolytica trophozoites. Hamsters intramuscularly immunized with full-length Igl and C-Igl were found to be 92% and 96% immune to liver abscess formation, respectively. Immune-response evaluation revealed that C-Igl can generate significant humoral immune responses, with high levels of antibodies in sera from immunized hamsters inhibiting 80% of trophozoites adherence to mammalian cells and inducing 80% more complement-mediated lysis of trophozoites compared with the control. C-Igl was further assessed for its cellular response by cytokine-gene qPCR analysis. The productions of IL-4 (8.4-fold) and IL-10 (2-fold) in the spleen cells of immunized hamsters were enhanced after in vitro stimulation. IL-4 expression was also supported by increased programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 gene.
Conclusions/significance: Immunobiochemical characterization strongly suggests the potential of recombinant Igl, especially the C-terminal fragment, as a vaccine candidate against amoebiasis. Moreover, protection through Th2-cell participation enabled effective humoral immunity against amebic liver abscesses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunization with the Entamoeba histolytica surface metalloprotease EhMSP-1 protects hamsters from amebic liver abscess.Infect Immun. 2015 Feb;83(2):713-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02490-14. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25452550 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the PEΔIII-LC3-KDEL3 Chimeric Protein of Entamoeba histolytica-Lectin as a Vaccine Candidate against Amebic Liver Abscess.J Immunol Res. 2021 Mar 20;2021:6697900. doi: 10.1155/2021/6697900. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33824880 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a carbohydrate recognition domain-like region in Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc lectin intermediate subunit.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Nov 5;12(11):e0053824. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00538-24. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39365081 Free PMC article.
-
Prospect for an Entamoeba histolytica Gal-lectin-based vaccine.Parasite Immunol. 2003 Feb;25(2):55-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3024.2003.00607.x. Parasite Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12791100 Review.
-
Entamoeba histolytica: from adherence to enteropathy.J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):420-9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.420. J Infect Dis. 1989. PMID: 2536786 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation on Elongation Factor 1 Alpha of Entamoeba histolytica Interaction with the Intermediate Subunit of the Gal/GalNAc Lectin and Actin in Phagocytosis.Pathogens. 2020 Aug 27;9(9):702. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9090702. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32867020 Free PMC article.
-
The macrophage polarization in Entamoeba histolytica infection modulation by the C fragment of the intermediate subunit of Gal/GalNAc-inhibitable lectin.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 19;15:1430057. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1430057. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39100678 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of hemolytic activity of the intermediate subunit of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar lectins.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 27;12(7):e0181864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181864. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28750000 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Proteomics Reveals Metabolic Reprogramming in Host Cells Induced by Trophozoites and Intermediate Subunit of Gal/GalNAc Lectins from Entamoeba histolytica.mSystems. 2022 Apr 26;7(2):e0135321. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01353-21. Epub 2022 Mar 28. mSystems. 2022. PMID: 35343800 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of inflammatory reactions during development of liver abscess in hamsters inoculated with Entamoeba nuttalli.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Feb 8;12(2):e0006216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006216. eCollection 2018 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29420539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stanley SL Jr. Amoebiasis. Lancet. 2003;361(9362):1025–34. Epub 2003/03/28. - PubMed
-
- Wertheim HF, Horby P, Woodall JP. Atlas of human infectious diseases UK: Blackwell Publishing; 2012.
-
- Walsh JA. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986;8(2):228–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

