Three-Dimensional Imaging of the Intracellular Fate of Plasmid DNA and Transgene Expression: ZsGreen1 and Tissue Clearing Method CUBIC Are an Optimal Combination for Multicolor Deep Imaging in Murine Tissues
- PMID: 26824850
- PMCID: PMC4732687
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148233
Three-Dimensional Imaging of the Intracellular Fate of Plasmid DNA and Transgene Expression: ZsGreen1 and Tissue Clearing Method CUBIC Are an Optimal Combination for Multicolor Deep Imaging in Murine Tissues
Abstract
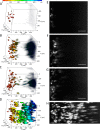
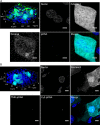
Evaluation methods for determining the distribution of transgene expression in the body and the in vivo fate of viral and non-viral vectors are necessary for successful development of in vivo gene delivery systems. Here, we evaluated the spatial distribution of transgene expression using tissue clearing methods. After hydrodynamic injection of plasmid DNA into mice, whole tissues were subjected to tissue clearing. Tissue clearing followed by confocal laser scanning microscopy enabled evaluation of the three-dimensional distribution of transgene expression without preparation of tissue sections. Among the tested clearing methods (ClearT2, SeeDB, and CUBIC), CUBIC was the most suitable method for determining the spatial distribution of transgene expression in not only the liver but also other tissues such as the kidney and lung. In terms of the type of fluorescent protein, the observable depth for green fluorescent protein ZsGreen1 was slightly greater than that for red fluorescent protein tdTomato. We observed a depth of ~1.5 mm for the liver and 500 μm for other tissues without preparation of tissue sections. Furthermore, we succeeded in multicolor deep imaging of the intracellular fate of plasmid DNA in the murine liver. Thus, tissue clearing would be a powerful approach for determining the spatial distribution of plasmid DNA and transgene expression in various murine tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Determining Transgene Expression Characteristics Using a Suction Device with Multiple Hole Adjusting a Left Lateral Lobe of the Mouse Liver.Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(6):944-950. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b18-00094. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 29863083
-
Tissue-Clearing Techniques Enable Three-Dimensional Visualization of Aerosolized Model Compound and Lung Structure at the Alveolar Scale.Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(1):24-28. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00348. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 29311480
-
Visualization of in vivo electroporation-mediated transgene expression in experimental tumors by optical and magnetic resonance imaging.Gene Ther. 2009 Jul;16(7):830-9. doi: 10.1038/gt.2009.55. Epub 2009 May 21. Gene Ther. 2009. PMID: 19458649
-
Theoretical considerations involving the pharmacokinetics of plasmid DNA.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005 Apr 5;57(5):675-88. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2004.12.003. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005. PMID: 15757754 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics of plasmid DNA-based non-viral gene medicine.Adv Genet. 2005;53:47-68. Adv Genet. 2005. PMID: 16240990 Review.
Cited by
-
Effective intraperitoneal gene transfection system using nanobubbles and ultrasound irradiation.Drug Deliv. 2017 Nov;24(1):737-744. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1319433. Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 28446052 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient gene transfection to the brain with ultrasound irradiation in mice using stabilized bubble lipopolyplexes prepared by the surface charge regulation method.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Apr 16;13:2309-2320. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S157375. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29713163 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrodynamic Delivery: Characteristics, Applications, and Technological Advances.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 31;15(4):1111. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041111. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-resolution 3D imaging of whole organ after clearing: taking a new look at the zebrafish testis.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 17;7:43012. doi: 10.1038/srep43012. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28211501 Free PMC article.
-
A non-viral DNA delivery system consisting of multifunctional chimeric peptide fused with zinc-finger protein.iScience. 2024 Mar 8;27(4):109464. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109464. eCollection 2024 Apr 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38558940 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

