Factors Associated with Therapeutic Efficacy of Intravesical OnabotulinumtoxinA Injection for Overactive Bladder Syndrome
- PMID: 26824901
- PMCID: PMC4732812
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147137
Factors Associated with Therapeutic Efficacy of Intravesical OnabotulinumtoxinA Injection for Overactive Bladder Syndrome
Abstract
Objectives: To analyze the predictors of therapeutic efficacy after intravesical botulinum toxin A injection for overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) refractory to antimuscarinic therapy.
Methods: All consecutively OAB patients, who visited the urologic outpatient clinics of a medical center and refractory to antimuscarinic treatment, were prospectively enrolled. All enrolled patients received intravesical injection of 100 U onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox). The Global Response Assessment (GRA) score ≥ 2 at 3 months after Botox injection was defined as a successful treatment, otherwise failed.
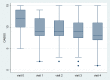
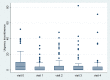
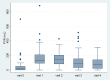
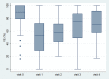
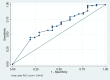
Results: Overall, 89 patients received intravesical injection. Eighty patients, including 42 men and 38 women, had received follow-up at 3 months. The overall success rate was 63.8%. The global response assessment, urgency severity score, urgency, urgency urinary incontinence and frequency episodes, and functional bladder capacity improved after treatment. However, post-void residual volume (PVR) increased, and voiding efficiency (VE) decreased after treatment. Female gender (odds ratio = 3.75) was the only independent factor associated with the success. Female gender (coefficient = 0.74), low baseline overactive bladder symptoms score (coefficient = -0.12) and the presence of OAB-wet (coefficient = 0.79) were independent factors associated with therapeutic efficacy (i.e., GRA score). VE (odds ratio = 0.062) was the only predictor for a large PVR at 3 months. The optimum cutoff value of VE was <87% with the area under the ROC curve being 0.64 (sensitivity = 63.8%, specificity = 57.1%).
Conclusions: The therapeutic effects of Botox can persist till 6 months after treatment. Female gender, low overactive bladder symptoms score and OAB-wet are associated better therapeutic efficacy, and low baseline VE is associated with large PVR. These findings can serve as an initial guide or assist in consultation regarding the treatment of OAB patients with Botox injection.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01657409.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of urgency severity is the most important factor in the subjective therapeutic outcome of intravesical onabotulinumtoxinA injection for overactive bladder.Neurourol Urodyn. 2017 Feb;36(2):338-343. doi: 10.1002/nau.22925. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017. PMID: 26575613
-
OnabotulinumtoxinA 100 U significantly improves all idiopathic overactive bladder symptoms and quality of life in patients with overactive bladder and urinary incontinence: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Eur Urol. 2013 Aug;64(2):249-56. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Eur Urol. 2013. PMID: 23608668 Clinical Trial.
-
Factors associated with a better therapeutic effect of solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder syndrome.Neurourol Urodyn. 2014 Mar;33(3):331-4. doi: 10.1002/nau.22394. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Neurourol Urodyn. 2014. PMID: 23494586
-
Intravesical OnabotulinumtoxinA Injection for Overactive Bladder Patients with Frailty, Medical Comorbidities or Prior Lower Urinary Tract Surgery.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Mar 25;8(4):91. doi: 10.3390/toxins8040091. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27023603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chapter 5: Clinical data in neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) and overactive bladder (OAB).Neurourol Urodyn. 2014 Jul;33 Suppl 3:S26-31. doi: 10.1002/nau.22630. Neurourol Urodyn. 2014. PMID: 25042140 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment of idiopathic overactive bladder with botulinum toxin: real-life results and patients' expectations.Porto Biomed J. 2022 May 18;7(2):e164. doi: 10.1097/j.pbj.0000000000000164. eCollection 2022 Mar-Apr. Porto Biomed J. 2022. PMID: 38304158 Free PMC article.
-
Urodynamic prognostic factors for large post-void residual urine volume after intravesical injection of onabotulinumtoxinA for overactive bladder.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 6;7:43753. doi: 10.1038/srep43753. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28262756 Free PMC article.
-
New Implantable Tibial Nerve Stimulation Devices: Review of Published Clinical Results in Comparison to Established Neuromodulation Devices.Res Rep Urol. 2019 Dec 23;11:351-357. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S231954. eCollection 2019. Res Rep Urol. 2019. PMID: 31921712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality of Life in Female Patients with Overactive Bladder after Botulinum Toxin Treatment.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Dec 21;16(1):7. doi: 10.3390/toxins16010007. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38276531 Free PMC article.
-
Individualizing medical treatment of overactive bladder.Tzu Chi Med J. 2018 Oct-Dec;30(4):195-199. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_83_18. Tzu Chi Med J. 2018. PMID: 30305780 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrams P, Abrams P, Cardozo L, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2002; 21: 167–178. - PubMed
-
- Chapple CR. Muscarinic receptor antagonist in the treatment of overactive bladder. Urology. 2000; 55:.33–50. - PubMed
-
- Yiangou Y, Facer P, Ford A, Brady C, Wiseman O, Fowler CJ, et al. Capsaicin receptor VR1 and ATP-gated ion channel P2X3 in human urinary bladder. BJU Int. 2001; 87: 774–779. - PubMed
-
- Apostolidis A, Popat R, Yiangou Y, Cockayne D, Ford AP, Davis JB, et al. Decreased sensory receptors P2X3 and TRPV1 in suburothelial nerve fibers following intradetrusor injections of Botulinum toxin for human detrusor overactivity. J Urol. 2005; 174: 977–982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

