A Complex Network of Interactions between S282 and G283 of Hepatitis C Virus Nonstructural Protein 5B and the Template Strand Affects Susceptibility to Sofosbuvir and Ribavirin
- PMID: 26824949
- PMCID: PMC4808174
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02436-15
A Complex Network of Interactions between S282 and G283 of Hepatitis C Virus Nonstructural Protein 5B and the Template Strand Affects Susceptibility to Sofosbuvir and Ribavirin
Abstract
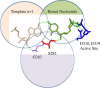
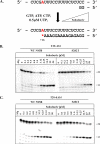
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase NS5B is essentially required for viral replication and serves as a prominent drug target. Sofosbuvir is a prodrug of a nucleotide analog that interacts selectively with NS5B and has been approved for HCV treatment in combination with ribavirin. Although the emergence of resistance to sofosbuvir is rarely seen in the clinic, the S282T mutation was shown to decrease susceptibility to this drug. S282T was also shown to confer hypersusceptibility to ribavirin, which is of potential clinical benefit. Here we devised a biochemical approach to elucidate the underlying mechanisms. Recent crystallographic data revealed a hydrogen bond between S282 and the 2'-hydroxyl of the bound nucleotide, while the adjacent G283 forms a hydrogen bond with the 2'-hydroxyl of the residue of the template that base pairs with the nucleotide substrate. We show that DNA-like modifications of the template that disrupt hydrogen bonding with G283 cause enzyme pausing with natural nucleotides. However, the specifically introduced DNA residue of the template reestablishes binding and incorporation of sofosbuvir in the context of S282T. Moreover, the DNA-like modifications of the template prevent the incorporation of ribavirin in the context of the wild-type enzyme, whereas the S282T mutant enables the binding and incorporation of ribavirin under the same conditions. Together, these findings provide strong evidence to show that susceptibility to sofosbuvir and ribavirin depends crucially on a network of interdependent hydrogen bonds that involve the adjacent residues S282 and G283 and their interactions with the incoming nucleotide and complementary template residue, respectively.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resistance analysis and characterization of NITD008 as an adenosine analog inhibitor against hepatitis C virus.Antiviral Res. 2016 Feb;126:43-54. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.12.010. Epub 2015 Dec 24. Antiviral Res. 2016. PMID: 26724382
-
In vitro selection of resistance to sofosbuvir in HCV replicons of genotype-1 to -6.Antivir Ther. 2017;22(7):587-597. doi: 10.3851/IMP3149. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Antivir Ther. 2017. PMID: 28248189
-
In vivo emergence of a novel mutant L159F/L320F in the NS5B polymerase confers low-level resistance to the HCV polymerase inhibitors mericitabine and sofosbuvir.J Infect Dis. 2014 Mar 1;209(5):668-75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit562. Epub 2013 Oct 23. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24154738 Clinical Trial.
-
Sofosbuvir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: new dog, new tricks.Clin Infect Dis. 2014 Aug 1;59(3):411-5. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu265. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Clin Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24748524 Review.
-
Interferon-free strategies with a nucleoside/nucleotide analogue.Semin Liver Dis. 2014 Feb;34(1):37-46. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1371009. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Semin Liver Dis. 2014. PMID: 24782257 Review.
Cited by
-
Akt Phosphorylation of Hepatitis C Virus NS5B Regulates Polymerase Activity and Hepatitis C Virus Infection.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 22;12:754664. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.754664. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34745059 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of Hepatitis C Virus for Developed Antiviral Agents Resistance Mutations and New Insights into in-silico Prediction Studies.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Nov 23;13:4235-4248. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S267809. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 33262618 Free PMC article.
-
Novel NS5B Resistance-Associated Substitution Emerges Under Failing Sofosbuvir/Ledipasvir Therapy.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2019 Mar 29;13(3):74-78. doi: 10.1002/cld.768. eCollection 2019 Mar. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2019. PMID: 30988941 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Mechanism of Inhibition of the Active Triphosphate Form of 2'-α-Fluoro,2'-β-bromouridine against Yellow Fever Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase.ACS Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 13;11(6):1528-1538. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.5c00086. Epub 2025 May 5. ACS Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40323779 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations Identified in the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Polymerase of Patients with Chronic HCV Treated with Ribavirin Cause Resistance and Affect Viral Replication Fidelity.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Nov 17;64(12):e01417-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01417-20. Print 2020 Nov 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32928732 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- McHutchison JG, Lawitz EJ, Shiffman ML, Muir AJ, Galler GW, McCone J, Nyberg LM, Lee WM, Ghalib RH, Schiff ER, Galati JS, Bacon BR, Davis MN, Mukhopadhyay P, Koury K, Noviello S, Pedicone LD, Brass CA, Albrecht JK, Sulkowski MS, Team IS. 2009. Peginterferon alfa-2b or alfa-2a with ribavirin for treatment of hepatitis C infection. N Engl J Med 361:580–593. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0808010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sulkowski MS, Sherman KE, Dieterich DT, Bsharat M, Mahnke L, Rockstroh JK, Gharakhanian S, McCallister S, Henshaw J, Girard PM, Adiwijaya B, Garg V, Rubin RA, Adda N, Soriano V. 2013. Combination therapy with telaprevir for chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection in patients with HIV: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 159:86–96. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-159-2-201307160-00654. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

