Two different specific JNK activators are required to trigger apoptosis or compensatory proliferation in response to Rbf1 in Drosophila
- PMID: 26825229
- PMCID: PMC4825841
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1100776
Two different specific JNK activators are required to trigger apoptosis or compensatory proliferation in response to Rbf1 in Drosophila
Abstract
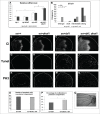
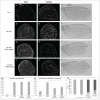
The Jun Kinase (JNK) signaling pathway responds to diverse stimuli by appropriate and specific cellular responses such as apoptosis, differentiation or proliferation. The mechanisms that mediate this specificity remain largely unknown. The core of this signaling pathway, composed of a JNK protein and a JNK kinase (JNKK), can be activated by various putative JNKK kinases (JNKKK) which are themselves downstream of different adaptor proteins. A proposed hypothesis is that the JNK pathway specific response lies in the combination of a JNKKK and an adaptor protein upstream of the JNKK. We previously showed that the Drosophila homolog of pRb (Rbf1) and a mutant form of Rbf1 (Rbf1(D253A)) have JNK-dependent pro-apoptotic properties. Rbf1(D253A) is also able to induce a JNK-dependent abnormal proliferation. Here, we show that Rbf1-induced apoptosis triggers proliferation which depends on the JNK pathway activation. Taking advantage of these phenotypes, we investigated the JNK signaling involved in either Rbf1-induced apoptosis or in proliferation in response to Rbf1-induced apoptosis. We demonstrated that 2 different JNK pathways involving different adaptor proteins and kinases are involved in Rbf1-apoptosis (i.e. Rac1-dTak1-dMekk1-JNK pathway) and in proliferation in response to Rbf1-induced apoptosis (i.e., dTRAF1-Slipper-JNK pathway). Using a transient induction of rbf1, we show that Rbf1-induced apoptosis activates a compensatory proliferation mechanism which also depends on Slipper and dTRAF1. Thus, these 2 proteins seem to be key players of compensatory proliferation in Drosophila.
Keywords: Apoptosis; JNK; Rac1; Rbf1; compensatory proliferation; dTRAF1.
Figures





Comment in
-
Putting Rb in context with JNK.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(24):3783. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1113786. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 26697834 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Reaper-mediated inhibition of DIAP1-induced DTRAF1 degradation results in activation of JNK in Drosophila.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Sep;4(9):705-10. doi: 10.1038/ncb842. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12198495
-
The Drosophila retinoblastoma protein, Rbf1, induces a Debcl- and Drp1-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis.J Cell Sci. 2015 Sep 1;128(17):3239-49. doi: 10.1242/jcs.169896. Epub 2015 Jul 24. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 26208635
-
A genetic screen targeting the tumor necrosis factor/Eiger signaling pathway: identification of Drosophila TAB2 as a functionally conserved component.Genetics. 2005 Dec;171(4):1683-94. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.045534. Epub 2005 Aug 3. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 16079232 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-apoptotic and pro-proliferation functions of the JNK pathway of Drosophila: roles in cell competition, tumorigenesis and regeneration.Open Biol. 2019 Mar 29;9(3):180256. doi: 10.1098/rsob.180256. Open Biol. 2019. PMID: 30836847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptosis-induced compensatory proliferation. The Cell is dead. Long live the Cell!Trends Cell Biol. 2008 Oct;18(10):467-73. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.08.001. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Trends Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18774295 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin K2 Prevents Lymphoma in Drosophila.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 6;7(1):17047. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17270-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29213118 Free PMC article.
-
Killers creating new life: caspases drive apoptosis-induced proliferation in tissue repair and disease.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Aug;24(8):1390-1400. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.47. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28362431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keeping Cell Death Alive: An Introduction into the French Cell Death Research Network.Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 28;12(7):901. doi: 10.3390/biom12070901. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass Purification Protocol for Drosophila melanogaster Wing Imaginal Discs: An Alternative to Dissection to Obtain Large Numbers of Disc Cells.Biology (Basel). 2022 Sep 22;11(10):1384. doi: 10.3390/biology11101384. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290290 Free PMC article.
-
Reproduction disrupts stem cell homeostasis in testes of aged male Drosophila via an induced microenvironment.PLoS Genet. 2019 Jul 11;15(7):e1008062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008062. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31295251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherr CJ, McCormick F. The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell 2002; 2:103-12; PMID:12204530; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1535-6108(02)00102-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cobrinik D. Pocket proteins and cell cycle control. Oncogene 2005; 24:2796-809; PMID:15838516; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208619 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Almasan A, Yin Y, Kelly RE, Lee EY, Bradley A, Li W, Bertino JR, Wahl GM. Deficiency of retinoblastoma protein leads to inappropriate S-phase entry, activation of E2F-responsive genes, and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1995; 92:5436-40; PMID:7777526; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.12.5436 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ianari A, Natale T, Calo E, Ferretti E, Alesse E, Screpanti I, Haigis K, Gulino A, Lees JA. Proapoptotic function of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein. Cancer Cell 2009; 15:184-94; PMID:19249677; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.01.026 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hilgendorf KI, Leshchiner ES, Nedelcu S, Maynard MA, Calo E, Ianari A, Walensky LD, Lees JA. The retinoblastoma protein induces apoptosis directly at the mitochondria. Genes Dev 2013; 27:1003-15; PMID:23618872; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.211326.112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
