Anionic fluoroquinolones as antibacterials against biofilm-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 26826023
- PMCID: PMC4753842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.01.012
Anionic fluoroquinolones as antibacterials against biofilm-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
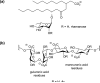
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common biofilm-forming bacterial pathogen implicated in diseases of the lungs. The extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of respiratory Pseudomonas biofilms are largely comprised of anionic molecules such as rhamnolipids and alginate that promote a mucoid phenotype. In this Letter, we examine the ability of negatively-charged fluoroquinolones to transverse the EPS and inhibit the growth of mucoid P. aeruginosa. Anionic fluoroquinolones were further compared with standard antibiotics via a novel microdiffusion assay to evaluate drug penetration through pseudomonal alginate and respiratory mucus from a patient with cystic fibrosis.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Biofilm; Fluoroquinolone; Mucoid; Pseudomonas.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

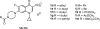



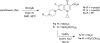
References
-
- Driscoll JA, Brody SL, Kollef MH. Drugs. 2007;67:351. - PubMed
-
- Vinckx T, Wei Q, Matthijs S, Cornelis P. Microbiology. 2010;156:678. - PubMed
-
- Mathee K, Ciofu O, Sternberg C, Lindum PW, Campbell JI, Jensen P, Johnsen AH, Givskov M, Ohman DE, Molin S, Høiby N, Kharazmi A. Microbiology. 1999;145:1349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

