Cc2d1a Loss of Function Disrupts Functional and Morphological Development in Forebrain Neurons Leading to Cognitive and Social Deficits
- PMID: 26826102
- PMCID: PMC6250986
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhw009
Cc2d1a Loss of Function Disrupts Functional and Morphological Development in Forebrain Neurons Leading to Cognitive and Social Deficits
Abstract
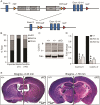
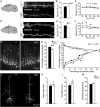
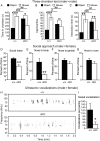
Loss-of-function (LOF) mutations in CC2D1A cause a spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders, including intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorder, and seizures, identifying a critical role for this gene in cognitive and social development. CC2D1A regulates intracellular signaling processes that are critical for neuronal function, but previous attempts to model the human LOF phenotypes have been prevented by perinatal lethality in Cc2d1a-deficient mice. To overcome this challenge, we generated a floxed Cc2d1a allele for conditional removal of Cc2d1a in the brain using Cre recombinase. While removal of Cc2d1a in neuronal progenitors using Cre expressed from the Nestin promoter still causes death at birth, conditional postnatal removal of Cc2d1a in the forebrain via calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-alpha (CamKIIa) promoter-driven Cre generates animals that are viable and fertile with grossly normal anatomy. Analysis of neuronal morphology identified abnormal cortical dendrite organization and a reduction in dendritic spine density. These animals display deficits in neuronal plasticity and in spatial learning and memory that are accompanied by reduced sociability, hyperactivity, anxiety, and excessive grooming. Cc2d1a conditional knockout mice therefore recapitulate features of both cognitive and social impairment caused by human CC2D1A mutation, and represent a model that could provide much needed insights into the developmental mechanisms underlying nonsyndromic neurodevelopmental disorders.
Keywords: autism; cognitive development; dendritic spines; intellectual disability; long-term plasticity.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Loss of CC2D1A in Glutamatergic Neurons Results in Autistic-Like Features in Mice.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Jul;18(3):2021-2039. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01072-z. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 34132974 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional Deletion of CC2D1A Reduces Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity and Impairs Cognitive Function through Rac1 Hyperactivation.J Neurosci. 2019 Jun 19;39(25):4959-4975. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2395-18.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30992372 Free PMC article.
-
CC2D1A regulates human intellectual and social function as well as NF-κB signaling homeostasis.Cell Rep. 2014 Aug 7;8(3):647-55. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.039. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 25066123 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity of dendritic spines: Molecular function and dysfunction in neurodevelopmental disorders.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019 Sep;73(9):541-550. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12899. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31215705 Review.
-
The Synaptic and Neuronal Functions of the X-Linked Intellectual Disability Protein Interleukin-1 Receptor Accessory Protein Like 1 (IL1RAPL1).Dev Neurobiol. 2019 Jan;79(1):85-95. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22657. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Dev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30548231 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of CC2D1A in Glutamatergic Neurons Results in Autistic-Like Features in Mice.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Jul;18(3):2021-2039. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01072-z. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 34132974 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional Deletion of CC2D1A Reduces Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity and Impairs Cognitive Function through Rac1 Hyperactivation.J Neurosci. 2019 Jun 19;39(25):4959-4975. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2395-18.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30992372 Free PMC article.
-
CC2D1A causes ciliopathy, intellectual disability, heterotaxy, renal dysplasia, and abnormal CSF flow.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Aug 21;7(10):e202402708. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202402708. Print 2024 Oct. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39168639 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin treatment rescues irritability-like behavior in Cc2d1a conditional knockout mice.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Oct;49(11):1792-1802. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01920-4. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39014123
-
Transcriptional and Post-Transcriptional Mechanisms of the Development of Neocortical Lamination.Front Neuroanat. 2017 Nov 9;11:102. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00102. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroanat. 2017. PMID: 29170632 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Betancur C. 2011. Etiological heterogeneity in autism spectrum disorders: more than 100 genetic and genomic disorders and still counting. Brain Res. 1380:42–77. - PubMed
-
- Bevins R, Besheer J. 2006. Object recognition in rats and mice: a one-trial non-matching-to-sample learning task to study “recognition memory”. Nat Protoc. 1:1306–1311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

