Increased CSF neurogranin concentration is specific to Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 26826204
- PMCID: PMC4793782
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002423
Increased CSF neurogranin concentration is specific to Alzheimer disease
Abstract
Objective: To assess the specificity of the dendritic protein neurogranin (Ng) in CSF from patients with a broad range of neurodegenerative diseases including a variety of dementias, tauopathies, and synucleinopathies.
Method: An optimized immunoassay was used to analyze CSF Ng in a retrospective cohort of 331 participants with different neurodegenerative diseases, including healthy controls (n = 19), biomarker-proven Alzheimer disease (AD) (n = 100), genetic AD (n = 2), behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (n = 20), speech variant frontotemporal dementia (n = 21), Lewy body dementia (n = 13), Parkinson disease (n = 31), progressive supranuclear palsy (n = 46), multiple system atrophy (n = 29), as well as a heterogeneous group with non-neurodegenerative cognitive impairment (n = 50). CSF Ng concentrations and correlations of CSF Ng with total tau, phosphorylated tau, and β-amyloid 42 concentrations, Mini-Mental State Examination score, and disease duration in the different groups were investigated.
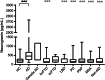
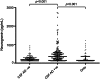
Results: Median CSF Ng concentration was higher in patients with AD compared to both controls (p < 0.001) and all other disease groups (all p < 0.001) except speech variant frontotemporal dementia. There were no significant differences in CSF Ng concentrations between any other neurodegenerative groups and controls. In addition, we found strong correlations between Ng and total tau (p < 0.001) and phosphorylated tau (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: These results confirm an increase in CSF Ng concentration in patients with AD as previously reported and show that this is specific to AD and not seen in a range of other neurodegenerative diseases.
© 2016 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Dekosky ST, Scheff SW. Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer's disease: correlation with cognitive severity. Ann Neurol 1990;27:457–464. - PubMed
-
- Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, et al. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer's disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol 1991;30:572–580. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease is a synaptic failure. Science 2002;298:789–791. - PubMed
-
- Scheff SW, Price DA, Dekosky ST, Mufson EJ. Synaptic alterations in CA1 in mild Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2007;68:1501–1508. - PubMed
-
- Blennow K, Bogdanovic N, Alafuzoff I, Ekman R, Davidsson P. Synaptic pathology in Alzheimer's disease: relation to severity of dementia, but not to senile plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, or the ApoE4 allele. J Neural Transm 1996;103:603–618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
