Alcaligenes faecalis ZD02, a Novel Nematicidal Bacterium with an Extracellular Serine Protease Virulence Factor
- PMID: 26826227
- PMCID: PMC4807518
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03444-15
Alcaligenes faecalis ZD02, a Novel Nematicidal Bacterium with an Extracellular Serine Protease Virulence Factor
Abstract
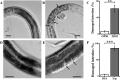
Root knot nematodes (RKNs) are the world's most damaging plant-parasitic nematodes (PPNs), and they can infect almost all crops. At present, harmful chemical nematicides are applied to control RKNs. Using microbial nematicides has been proposed as a better management strategy than chemical control. In this study, we describe a novel nematicidal bacterium named Alcaligenes faecalis ZD02. A. faecalis ZD02 was isolated from Caenorhabditis elegans cadavers and has nematostatic and nematicidal activity, as confirmed by C. elegans growth assay and life span assay. In addition, A. faecalis ZD02 fermentation broth showed toxicity against C. elegans and Meloidogyne incognita. To identify the nematicidal virulence factor, the genome of strain ZD02 was sequenced. By comparing all of the predicted proteins of strain ZD02 to reported nematicidal virulence factors, we determined that an extracellular serine protease (Esp) has potential to be a nematicidal virulence factor, which was confirmed by bioassay on C. elegans and M. incognita. Using C. elegans as the target model, we found that both A. faecalis ZD02 and the virulence factor Esp can damage the intestines of C. elegans. The discovery that A. faecalis ZD02 has nematicidal activity provides a novel bacterial resource for the control of RKNs.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The complete genome sequence of Alcaligenes faecalis ZD02, a novel potential bionematocide.J Biotechnol. 2016 Jan 20;218:73-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.12.001. Epub 2015 Dec 4. J Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26656226
-
The Nif3-Family Protein YqfO03 from Pseudomonas syringae MB03 Has Multiple Nematicidal Activities against Caenorhabditis elegans and Meloidogyne incognita.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 6;19(12):3915. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123915. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30563288 Free PMC article.
-
Nematicidal effects of a peptidase (NlpC/P60) from the phytopathogen Pseudomonas syringae MB03 on the model nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and plant-parasitic Meloidogyne incognita.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):6313-6324. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07439-5. Epub 2022 May 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35532867
-
Nematicidal enzymes from microorganisms and their applications.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Aug;97(16):7081-95. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5045-0. Epub 2013 Jul 6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23832084 Review.
-
Naturally-occurring nematicides of plant origin: two decades of novel chemistries.Pest Manag Sci. 2025 Feb;81(2):540-571. doi: 10.1002/ps.8504. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Pest Manag Sci. 2025. PMID: 39503300 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
3-(Methylthio)Propionic Acid from Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner Exhibits High Nematicidal Activity against the Root Knot Nematode Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid and White) Chitwood.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 30;25(3):1708. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031708. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338986 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Understanding the Function of Aegerolysins.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Sep 11;14(9):629. doi: 10.3390/toxins14090629. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36136567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome sequencing and analysis of Alcaligenes faecalis subsp. phenolicus MB207.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 26;8(1):3616. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21919-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29483539 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of bioprotective microbial organisms in Upper Region of Assam and its efficacy against Meloidogyne graminicola.PeerJ. 2023 Jul 28;11:e15779. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15779. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37529212 Free PMC article.
-
'A plant's major strength in rhizosphere': the plant growth promoting rhizobacteria.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Apr 4;205(5):165. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03502-2. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37012531 Review.
References
-
- Abad P, Gouzy J, Aury JM, Castagnone-Sereno P, Danchin EG, Deleury E, Perfus-Barbeoch L, Anthouard V, Artiguenave F, Blok VC, Caillaud MC, Coutinho PM, Dasilva C, De Luca F, Deau F, Esquibet M, Flutre T, Goldstone JV, Hamamouch N, Hewezi T, Jaillon O, Jubin C, Leonetti P, Magliano M, Maier TR, Markov GV, McVeigh P, Pesole G, Poulain J, Robinson-Rechavi M, Sallet E, Segurens B, Steinbach D, Tytgat T, Ugarte E, van Ghelder C, Veronico P, Baum TJ, Blaxter M, Bleve-Zacheo T, Davis EL, Ewbank JJ, Favery B, Grenier E, Henrissat B, Jones JT, Laudet V, Maule AG, Quesneville H, Rosso MN, et al. . 2008. Genome sequence of the metazoan plant-parasitic nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Nat Biotechnol 26:909–915. doi:10.1038/nbt.1482. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

