A new structural model of Alzheimer's Aβ42 fibrils based on electron paramagnetic resonance data and Rosetta modeling
- PMID: 26827680
- PMCID: PMC4764428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsb.2016.01.013
A new structural model of Alzheimer's Aβ42 fibrils based on electron paramagnetic resonance data and Rosetta modeling
Abstract
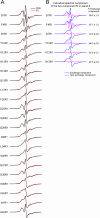
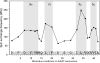
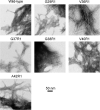
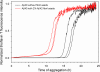
Brain deposition of Aβ in the form of amyloid plaques is a pathological hallmark of Alzheimer's disease. There are two major species of Aβ in the brain: Aβ42 and Aβ40. Although Aβ40 is several-fold more abundant than Aβ42 in soluble form, Aβ42 is the major component of amyloid plaques. Structural knowledge of Aβ42 fibrils is important both for understanding the process of Aβ aggregation and for designing fibril-targeting drugs. Here we report site-specific structural information of Aβ42 fibrils at 22 residue positions based on electron paramagnetic resonance data. In combination with structure prediction program Rosetta, we modeled Aβ42 fibril structure at atomic resolution. Our Aβ42 fibril model consists of four parallel in-register β-sheets: βN (residues ∼7-13), β1 (residues ∼17-20), β2 (residues ∼32-36), and βC (residues 39-41). The region of β1-loop-β2 in Aβ42 fibrils adopts similar structure as that in Aβ40 fibrils. This is consistent with our cross seeding data that Aβ42 fibril seeds shortened the lag phase of Aβ40 fibrillization. On the other hand, Aβ42 fibrils contain a C-terminal β-arc-β motif with a special turn, termed "arc", at residues 37-38, which is absent in Aβ40 fibrils. Our results can explain both the higher aggregation propensity of Aβ42 and the importance of Aβ42 to Aβ40 ratio in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; Amyloid; Aβ; Protein aggregation; Spin labeling.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alzheimer's Aβ42 and Aβ40 peptides form interlaced amyloid fibrils.J Neurochem. 2013 Aug;126(3):305-11. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12202. Epub 2013 Mar 12. J Neurochem. 2013. PMID: 23406382 Free PMC article.
-
Structural origin of polymorphism of Alzheimer's amyloid β-fibrils.Biochem J. 2012 Oct 1;447(1):43-50. doi: 10.1042/BJ20120034. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22823461
-
Alzheimer's Aβ42 and Aβ40 form mixed oligomers with direct molecular interactions.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 1;534:292-296. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.092. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33272573 Free PMC article.
-
The turn formation at positions 22 and 23 in the 42-mer amyloid beta peptide: the emerging role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2010 Jul;10 Suppl 1:S169-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0594.2010.00598.x. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2010. PMID: 20590832 Review.
-
Aβ42 and Aβ40: similarities and differences.J Pept Sci. 2015 Jul;21(7):522-9. doi: 10.1002/psc.2789. Epub 2015 May 28. J Pept Sci. 2015. PMID: 26018760 Review.
Cited by
-
Pulsatile stretch as a novel modulator of amyloid precursor protein processing and associated inflammatory markers in human cerebral endothelial cells.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 26;8(1):1689. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20117-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29374229 Free PMC article.
-
On the Conformational Dynamics of β-Amyloid Forming Peptides: A Computational Perspective.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Jun 3;8:532. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00532. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32656188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Structural Polymorphism in Driving the Mechanical Performance of the Alzheimer's Beta Amyloid Fibrils.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Apr 24;7:83. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00083. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31106199 Free PMC article.
-
Out-of-Register Parallel β-Sheets and Antiparallel β-Sheets Coexist in 150-kDa Oligomers Formed by Amyloid-β(1-42).J Mol Biol. 2020 Jul 24;432(16):4388-4407. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.018. Epub 2020 May 26. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32470558 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Zn2+-Dependent Amyloid-β1-42 Neurotoxicity in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 Jan;199(1):53-61. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02131-w. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 32281074 Review.
References
-
- Agopian A, Guo Z. Structural origin of polymorphism for Alzheimer's amyloid-β fibrils. Biochem. J. 2012;447:43–50. - PubMed
-
- Antzutkin ON, Leapman RD, Balbach JJ, Tycko R. Supramolecular structural constraints on Alzheimer's β-amyloid fibrils from electron microscopy and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 2002;41:15436–15450. - PubMed
-
- Baker RT, Catanzariti AM, Karunasekara Y, Soboleva TA, Sharwood R, et al. Using deubiquitylating enzymes as research tools. Methods Enzymol. 2005;398:540–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

