Isoxazole Alters Metabolites and Gene Expression, Decreasing Proliferation and Promoting a Neuroendocrine Phenotype in β-Cells
- PMID: 26828310
- PMCID: PMC5198576
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00993
Isoxazole Alters Metabolites and Gene Expression, Decreasing Proliferation and Promoting a Neuroendocrine Phenotype in β-Cells
Abstract
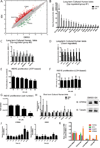
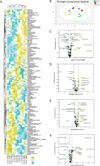
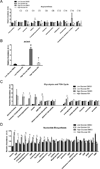
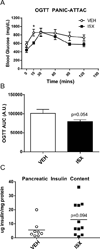
Novel strategies are needed to modulate β-cell differentiation and function as potential β-cell replacement or restorative therapies for diabetes. We previously demonstrated that small molecules based on the isoxazole scaffold drive neuroendocrine phenotypes. The nature of the effects of isoxazole compounds on β-cells was incompletely defined. We find that isoxazole induces genes that support neuroendocrine and β-cell phenotypes and suppresses genes important for proliferation. Isoxazole alters β-cell metabolites and protects glucose-responsive signaling pathways under lipotoxic conditions. Finally, we show that isoxazole improves glycemia in a mouse model of β-cell regeneration. Isoxazole is a prime candidate to alter cell fate in different contexts.
Figures

References
-
- Vetere A, Choudhary A, Burns SM, Wagner BK. Targeting the pancreatic beta-cell to treat diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery. 2014;13:278–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

