Modeling of breath methane concentration profiles during exercise on an ergometer
- PMID: 26828421
- PMCID: PMC4913871
- DOI: 10.1088/1752-7155/10/1/017105
Modeling of breath methane concentration profiles during exercise on an ergometer
Abstract
We develop a simple three compartment model based on mass balance equations which quantitatively describes the dynamics of breath methane concentration profiles during exercise on an ergometer. With the help of this model it is possible to estimate the endogenous production rate of methane in the large intestine by measuring breath gas concentrations of methane.
Figures

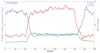

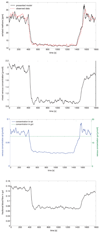
References
-
- Adams NG, Smith D, Paulson JF. An experimental survey of the reactions of ions (n = 0 to 4) with several diatomic and polyatomic molecules at 300 K. J Chem Phys. 1980;72:288–97.
-
- Anderson JC, Babb AL, Hlastala MP. Modeling soluble gas exchange in the airways and alveoli. Ann Biomed Eng. 2003;31:1402–22. - PubMed
-
- Boros M, Tuboly E, Mészáros A, Amann A. The role of methane in mammalian physiology—is it a gasotransmitter? J Breath Res. 2015;9:014001. - PubMed
-
- Chen O, et al. Methane attenuates myocardial ischemia injury in rats through anti-oxidative, anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory actions. Free Radical Biol Med. 2016;90:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
