3B11-N, a monoclonal antibody against MERS-CoV, reduces lung pathology in rhesus monkeys following intratracheal inoculation of MERS-CoV Jordan-n3/2012
- PMID: 26828465
- PMCID: PMC4769911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.01.004
3B11-N, a monoclonal antibody against MERS-CoV, reduces lung pathology in rhesus monkeys following intratracheal inoculation of MERS-CoV Jordan-n3/2012
Abstract
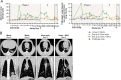
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) was identified in 2012 as the causative agent of a severe, lethal respiratory disease occurring across several countries in the Middle East. To date there have been over 1600 laboratory confirmed cases of MERS-CoV in 26 countries with a case fatality rate of 36%. Given the endemic region, it is possible that MERS-CoV could spread during the annual Hajj pilgrimage, necessitating countermeasure development. In this report, we describe the clinical and radiographic changes of rhesus monkeys following infection with 5×10(6) PFU MERS-CoV Jordan-n3/2012. Two groups of NHPs were treated with either a human anti-MERS monoclonal antibody 3B11-N or E410-N, an anti-HIV antibody. MERS-CoV Jordan-n3/2012 infection resulted in quantifiable changes by computed tomography, but limited other clinical signs of disease. 3B11-N treated subjects developed significantly reduced lung pathology when compared to infected, untreated subjects, indicating that this antibody may be a suitable MERS-CoV treatment.
Keywords: Animal model, MERS; Antibody therapy; Human monoclonal antibody therapy; MERS-CoV; Respiratory syndrome.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Bossart K.N., Zhu Z., Middleton D., Klippel J., Crameri G., Bingham J., McEachern J.A., Green D., Hancock T.J., Chan Y.P., Hickey A.C., Dimitrov D.S., Wang L.F., Broder C.C. A neutralizing human monoclonal antibody protects against lethal disease in a new ferret model of acute nipah virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000642. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

