Pluripotency markers are differentially induced by MEK inhibition in thyroid and melanoma BRAFV600E cell lines
- PMID: 26828826
- PMCID: PMC4910922
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1139230
Pluripotency markers are differentially induced by MEK inhibition in thyroid and melanoma BRAFV600E cell lines
Abstract
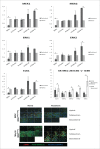
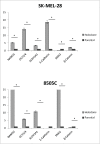
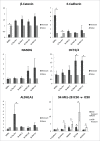
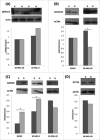
Oncogenic mutations in BRAF are common in melanoma and thyroid carcinoma and drive constitutive activation of the MAPK pathway. Molecularly targeted therapies of this pathway improves survival compared to chemotherapy; however, responses tend to be short-lived as resistance invariably occursCell line models of melanoma and thyroid carcinoma, +/- BRAF(V600E) activating mutation, were treated with the MEK inhibitor PD0325901. Treated and naive samples were assayed for expression of key members of the MAPK pathway. Global microRNA expression profiling of naive and resistant cells was performed via next generation sequencingand indicated pluripotency pathways in resistance. Parental cell lines were progressed to holoclones to confirm the miRNA stemness profileMembers of the MIR302/373/374/520 family of embryonic stem cell specific cell cycle regulating (ESCC) microRNAs were identified as differentially expressed between resistant BRAF(V600E) melanoma and thyroid cell lines. Upregulated expression of gene and protein stemness markers, upregulated expression of MAPK pathway genes and downregulation of the ESCC MIR302 cluster in BRAF(V600E) melanoma indicated an increased stem-like phenotype in resistant BRAF(V600E) melanoma. Conversely, downregulated expression of gene and protein stemness markers, downregulated expression of MAPK pathway genes, upregulation of the ESCC MIR520 cluster, reeexpression of cell surface receptors, and induced differentiation-associated morphology in resistant BRAF(V600E) indicate a differentiated phenotype associated with MEK inhibitor resistance in BRAF(V600E) thyroid cellsThe differential patterns of resistance observed between BRAF(V600E) melanoma and thyroid cell lines may reflect tissue type or de novo differentiation, but could have significant impact on the response of primary and metastatic cells to MEK inhibitor treatment. This study provides a basis for the investigation of the cellular differentiation/self-renewal access and its role in resistance to MEK inhibition.
Keywords: BRAFV600E; MEK inhibition; cancer; cancer stem cell; microrna; pluripotency; resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overcoming acquired BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma via targeted inhibition of Hsp90 with ganetespib.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Feb;13(2):353-63. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0481. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24398428
-
Mitochondrial localization and regulation of BRAFV600E in thyroid cancer: a clinically used RAF inhibitor is unable to block the mitochondrial activities of BRAFV600E.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jan;96(1):E19-30. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-1071. Epub 2010 Oct 6. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 20926530
-
Selective growth inhibition in BRAF mutant thyroid cancer by the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Dec;92(12):4712-8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-1184. Epub 2007 Sep 18. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17878251
-
[Progress of anti-tumor study based on BRAF].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012 Dec;47(12):1567-74. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 23460959 Review. Chinese.
-
Vemurafenib.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014;201:215-25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54490-3_13. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24756795 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of the Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity Variant rs26232 with the Invasive Activity of Synovial Fibroblasts.Cells. 2019 Oct 22;8(10):1300. doi: 10.3390/cells8101300. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31652652 Free PMC article.
-
Pluripotency markers are differentially induced by IGF1 and bFGF in cells from patients' lesions of large/giant congenital melanocytic nevi.Biomark Res. 2019 Jan 14;7:2. doi: 10.1186/s40364-018-0152-9. eCollection 2019. Biomark Res. 2019. PMID: 30675361 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Phosphatases and Kinases: How to Checkmate Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 28;9:690306. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.690306. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34778245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Avian iPSC Derivation to Recover Threatened Wild Species: A Comprehensive Review in Light of Well-Established Protocols.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;14(2):220. doi: 10.3390/ani14020220. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcription factor CUX1 negatively regulates invasion in castrate resistant prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2020 Mar 3;11(9):846-857. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27494. eCollection 2020 Mar 3. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 32180898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Houben R, Becker J, Kappel A, Terheyden P, Bröcker E, Goetz R, Rapp U. Constitutive activation of the Ras-Raf signaling pathway in metastatic melanoma is associated with poor prognosis. J Carcinog 2004; 3:6; PMID:15046639; http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1477-3163-3-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tang K, Lee C. BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid carcinoma: pathogenic role and clinical implications. J Chin Med Assoc 2010; 73:113-28; PMID:20230995; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1726-4901(10)70025-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sawyers C. Targeted cancer therapy. Nature 2004; 432:294-7; PMID:15549090; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature03095 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, et al.. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med 2011; 364:2507-16; PMID:21639808; http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1103782 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nazarian R, Shi H, Wang Q, Kong X, Koya RC, Lee H, Chen Z, Lee MK, Attar N, Sazegar H, et al.. Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nature 2010; 468:973-7; PMID:21107323; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature09626 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
