Glutamatergic axon-derived BDNF controls GABAergic synaptic differentiation in the cerebellum
- PMID: 26830657
- PMCID: PMC4735332
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20201
Glutamatergic axon-derived BDNF controls GABAergic synaptic differentiation in the cerebellum
Abstract
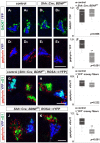
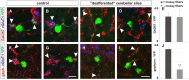
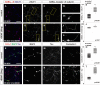
To study mechanisms that regulate the construction of inhibitory circuits, we examined the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the assembly of GABAergic inhibitory synapses in the mouse cerebellar cortex. We show that within the cerebellum, BDNF-expressing cells are restricted to the internal granular layer (IGL), but that the BDNF protein is present within mossy fibers which originate from cells located outside of the cerebellum. In contrast to deletion of TrkB, the cognate receptor for BDNF, deletion of Bdnf from cerebellar cell bodies alone did not perturb the localization of pre- or postsynaptic constituents at the GABAergic synapses formed by Golgi cell axons on granule cell dendrites within the IGL. Instead, we found that BDNF derived from excitatory mossy fiber endings controls their differentiation. Our findings thus indicate that cerebellar BDNF is derived primarily from excitatory neurons--precerebellar nuclei/spinal cord neurons that give rise to mossy fibers--and promotes GABAergic synapse formation as a result of release from axons. Thus, within the cerebellum the preferential localization of BDNF to axons enhances the specificity through which BDNF promotes GABAergic synaptic differentiation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Phenotype of cerebellar glutamatergic neurons is altered in stargazer mutant mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression.J Comp Neurol. 2005 Jan 10;481(2):145-59. doi: 10.1002/cne.20386. J Comp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15562504
-
Transgenic brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates a developing cerebellar inhibitory synapse.Learn Mem. 1999 May-Jun;6(3):276-83. Learn Mem. 1999. PMID: 10492009 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates mouse cerebellar granule cell GABA(A) receptor-mediated responses via postsynaptic mechanisms.J Physiol. 2003 May 1;548(Pt 3):711-21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.037846. Epub 2003 Mar 14. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12640011 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF signaling in the formation, maturation and plasticity of glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses.Exp Brain Res. 2009 Dec;199(3-4):203-34. doi: 10.1007/s00221-009-1994-z. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Exp Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19777221 Review.
-
Ultrastructural description of glutamate-, aspartate-, taurine-, and glycine-like immunoreactive terminals from five rat brain regions.J Electron Microsc Tech. 1990 May;15(1):49-66. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060150106. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1990. PMID: 1971014 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 16;25(4):2332. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042332. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38397008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Targets in Neurotrophin Signaling in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Aug;55(8):6939-6955. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0885-3. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29372544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced Cerebellar BDNF Availability Affects Postnatal Differentiation and Maturation of Granule Cells in a Mouse Model of Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Sep;60(9):5395-5410. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03435-3. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37314654 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebellar sub-divisions differ in exercise-induced plasticity of noradrenergic axons and in their association with resilience to activity-based anorexia.Brain Struct Funct. 2017 Jan;222(1):317-339. doi: 10.1007/s00429-016-1220-2. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. PMID: 27056728 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of motor learning in a mouse model of Rett syndrome following long-term treatment with a novel small-molecule activator of TrkB.Dis Model Mech. 2020 Nov 27;13(11):dmm044685. doi: 10.1242/dmm.044685. Dis Model Mech. 2020. PMID: 33361117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chao M. V., Rajagopal R. & Lee F. S. Neurotrophin signalling in health and disease. Clinical Sci 110, 167–173 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

