Magnetic resonance imaging of swallowing-related structures in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients receiving IMRT: Longitudinal dose-response characterization of quantitative signal kinetics
- PMID: 26830697
- PMCID: PMC4794348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2016.01.011
Magnetic resonance imaging of swallowing-related structures in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients receiving IMRT: Longitudinal dose-response characterization of quantitative signal kinetics
Abstract
Background: We aim to characterize serial (i.e., acute and late) MRI signal intensity (SI) changes in dysphagia-associated structures as a function of radiotherapy (RT) in nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) patients.
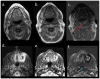
Materials and methods: We retrospectively extracted data on 72 patients with stage III-IV NPC treated with intensity-modulated RT (IMRT). The mean T1- and T2-weighted MRI SIs were recorded for the superior pharyngeal constrictor (SPC) and soft palate (SP) at baseline, early-after IMRT, and last follow up, with normalization to structures receiving <5 Gy.
Results: All structures had a significant increase in T2 SIs early after treatment, irrespective of the mean dose given. At last follow-up, the increase in T2 SI subsided completely for SPC and partially for SP. The T1 SI did not change significantly in early follow-up images of both structures; on late follow-up, patients with mean doses >62.25 Gy had a significant decrease in the corresponding T1 SI for SPC (1.6 ± 0.4 vs. 1.3 ± 0.4, P=0.007) but decreased non-significantly for SP.
Conclusions: Serial MRI acquisitions enable the identification of both early and late radiation-induced changes in swallowing structures after definitive IMRT for NPC. Dose dependent decrease in late T1 SI is associated with higher RT doses to the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle; while dose independent increase in SI for both structures in early post-RT T2 images is observed and subsides after therapy. Further efforts will seek to elucidate the relationship between dose-dependent muscle SI changes and functional alteration of swallowing muscles.
Keywords: Dose–response; Dysphagia; IMRT; Magnetic resonance imaging; Nasopharyngeal carcinoma; Superior pharyngeal constrictor.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Langendijk JA, Doornaert P, Verdonck-de Leeuw IM, Leemans CR, Aaronson NK, Slotman BJ. Impact of late treatment-related toxicity on quality of life among patients with head and neck cancer treated with radiotherapy. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2008;26:3770–6. - PubMed
-
- Levendag PC, Teguh DN, Voet P, van der Est H, Noever I, de Kruijf WJM, et al. Dysphagia disorders in patients with cancer of the oropharynx are significantly affected by the radiation therapy dose to the superior and middle constrictor muscle: A dose-effect relationship. Radiother Oncol. 2007;85:64–73. - PubMed
-
- Caudell JJ, Schaner PE, Meredith RF, Locher JL, Nabell LM, Carroll WR, et al. Factors associated with long-term dysphagia after definitive radiotherapy for locally advanced head-and-neck cancer. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics. 2009;73:410–5. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen NP, Moltz CC, Frank C, Vos P, Smith HJ, Karlsson U, et al. Dysphagia following chemoradiation for locally advanced head and neck cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004;15:383–8. - PubMed
-
- Langendijk JA, Doornaert P, Verdonck-de Leeuw IM, Leemans CR, Aaronson NK, Slotman BJ. Impact of late treatment-related toxicity on quality of life among patients with head and neck cancer treated with radiotherapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2008;26:3770–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

