ClinQC: a tool for quality control and cleaning of Sanger and NGS data in clinical research
- PMID: 26830926
- PMCID: PMC4735967
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-0915-y
ClinQC: a tool for quality control and cleaning of Sanger and NGS data in clinical research
Abstract
Background: Traditional Sanger sequencing has been used as a gold standard method for genetic testing in clinic to perform single gene test, which has been a cumbersome and expensive method to test several genes in heterogeneous disease such as cancer. With the advent of Next Generation Sequencing technologies, which produce data on unprecedented speed in a cost effective manner have overcome the limitation of Sanger sequencing. Therefore, for the efficient and affordable genetic testing, Next Generation Sequencing has been used as a complementary method with Sanger sequencing for disease causing mutation identification and confirmation in clinical research. However, in order to identify the potential disease causing mutations with great sensitivity and specificity it is essential to ensure high quality sequencing data. Therefore, integrated software tools are lacking which can analyze Sanger and NGS data together and eliminate platform specific sequencing errors, low quality reads and support the analysis of several sample/patients data set in a single run.
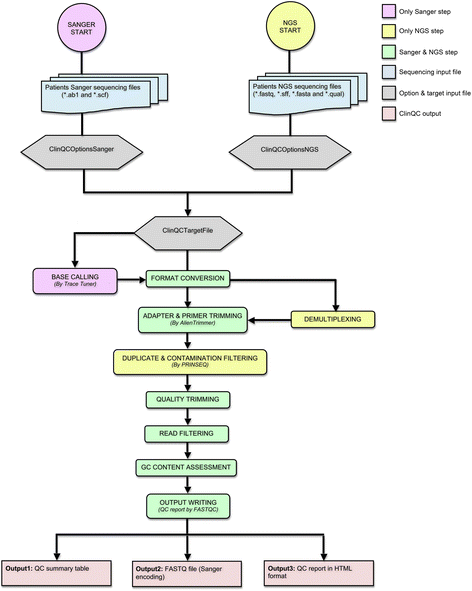
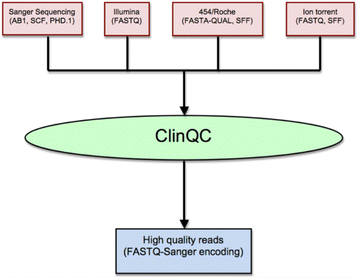
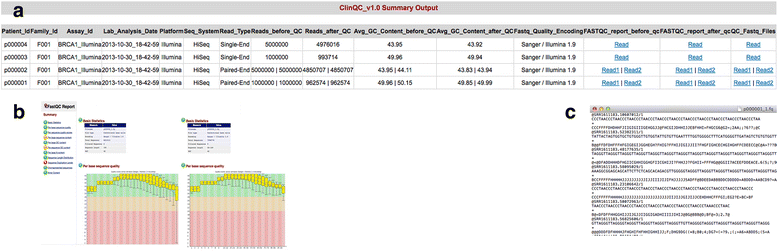
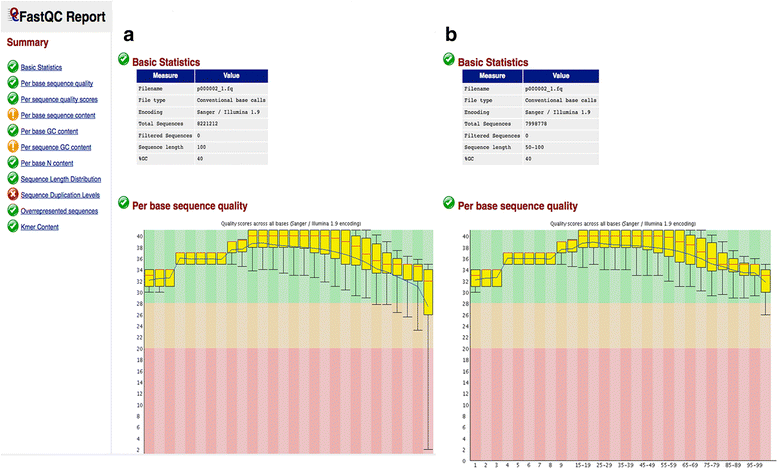
Results: We have developed ClinQC, a flexible and user-friendly pipeline for format conversion, quality control, trimming and filtering of raw sequencing data generated from Sanger sequencing and three NGS sequencing platforms including Illumina, 454 and Ion Torrent. First, ClinQC convert input read files from their native formats to a common FASTQ format and remove adapters, and PCR primers. Next, it split bar-coded samples, filter duplicates, contamination and low quality sequences and generates a QC report. ClinQC output high quality reads in FASTQ format with Sanger quality encoding, which can be directly used in down-stream analysis. It can analyze hundreds of sample/patients data in a single run and generate unified output files for both Sanger and NGS sequencing data. Our tool is expected to be very useful for quality control and format conversion of Sanger and NGS data to facilitate improved downstream analysis and mutation screening.
Conclusions: ClinQC is a powerful and easy to handle pipeline for quality control and trimming in clinical research. ClinQC is written in Python with multiprocessing capability, run on all major operating systems and is available at https://sourceforge.net/projects/clinqc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MutAid: Sanger and NGS Based Integrated Pipeline for Mutation Identification, Validation and Annotation in Human Molecular Genetics.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 3;11(2):e0147697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147697. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26840129 Free PMC article.
-
DaMold: A data-mining platform for variant annotation and visualization in molecular diagnostics research.Hum Mutat. 2017 Jul;38(7):778-787. doi: 10.1002/humu.23227. Epub 2017 May 30. Hum Mutat. 2017. PMID: 28397319
-
QC-Chain: fast and holistic quality control method for next-generation sequencing data.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060234. Epub 2013 Apr 2. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23565205 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of next-generation sequencing software in mapping and assembly.J Hum Genet. 2011 Jun;56(6):406-14. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2011.43. Epub 2011 Apr 28. J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21525877 Review.
-
HLA typing by next-generation sequencing - getting closer to reality.Tissue Antigens. 2014 Feb;83(2):65-75. doi: 10.1111/tan.12298. Tissue Antigens. 2014. PMID: 24447174 Review.
Cited by
-
PIPEBAR and OverlapPER: tools for a fast and accurate DNA barcoding analysis and paired-end assembly.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Aug 8;19(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2307-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30089465 Free PMC article.
-
A Large-Scale and Serverless Computational Approach for Improving Quality of NGS Data Supporting Big Multi-Omics Data Analyses.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 13;12:699280. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.699280. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34326863 Free PMC article.
-
Computational challenges in detection of cancer using cell-free DNA methylation.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Dec 7;20:26-39. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.12.001. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34976309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FQStat: a parallel architecture for very high-speed assessment of sequencing quality metrics.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Aug 15;20(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-3015-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31416440 Free PMC article.
-
On the study of microbial transcriptomes using second- and third-generation sequencing technologies.J Microbiol. 2016 Aug;54(8):527-36. doi: 10.1007/s12275-016-6233-2. Epub 2016 Aug 2. J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27480632 Review.
References
-
- Johnston JJ, Rubinstein WS, Facio FM, Ng D, Singh LN, Teer JK, et al. Secondary variants in individuals undergoing exome sequencing: screening of 572 individuals identifies high-penetrance mutations in cancer-susceptibility genes. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;91(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.05.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

