Evaluation of treatments for sacroiliitis in spondyloarthropathy using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium Canada scoring system
- PMID: 26832154
- PMCID: PMC4734856
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-0916-2
Evaluation of treatments for sacroiliitis in spondyloarthropathy using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium Canada scoring system
Abstract
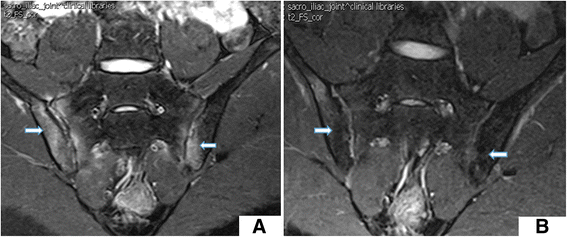
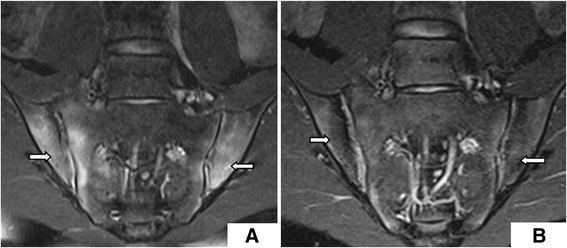
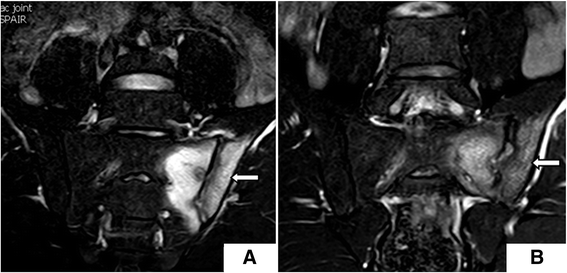
Background: In this study, the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium Canada (SPARCC) scoring method was used to compare treatment methods in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (SpA), a form of sacroiliitis. MRI abnormalities in bone marrow edema (BME) were compared before and after treatment in order to compare the efficacy of anti-TNF-α and DMARD, alone or in combination, as treatments for sacroiliitis.
Methods: Fifty-six Chinese patients with axial SpA (mean age 22.6 years) were recruited. Patients were divided into three groups according to different treatments (anti-TNF-α alone vs. DMARDs alone vs. combined anti-TNF-α and DMARDs). MRI examinations were performed before and after treatment. The SPARCC score, clinically relevant AS Disease Activity (ASDAS) indices, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP) were analyzed.
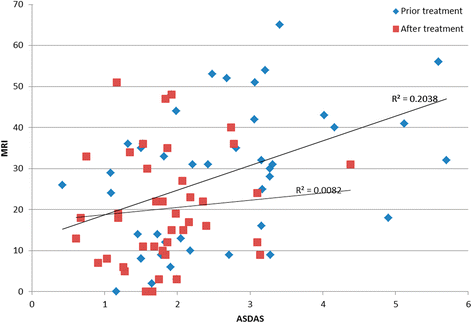
Results: After treatment, ASDAS and SPARCC scores, ESR, and CRP were significantly improved (P < 0.05) in the anti-TNF-α monotherapy and combination groups; however, there were no statistically significant differences (P > 0.05) in clinical disease activity and radiological inflammation of sacroiliac joint (SIJ) in patients in the DMARDs alone group. SPARCC showed a correlation with ASDAS score pre-treatment, but not post-treatment. Furthermore, there were significant changes (P < 0.05) in these patients with axial SpA after only 3 months of treatment. Follow-up studies of patients who continued therapy for 4-6 months and 9-12 months revealed statistically significant differences from baseline (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: SPARCC can be used to assess severity of disease pre-treatment. Anti-TNF-α treatment resulted in effective reduction of disease activity and BME of SIJ after 3 months of therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of active inflammation, chronic structural damage, and response to treatment of sacroiliitis in axial spondyloarthritis using the Spondyloarthritis research consortium of Canada scoring system.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Jul 8;23(1):654. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05609-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 35804360 Free PMC article.
-
Local infliximab injection of sacroiliac joints in non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: Impact on clinical and magnetic resonance imaging parameters of disease activity.Mod Rheumatol. 2015 May;25(3):421-6. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2014.972495. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Mod Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25401227
-
Baseline severity of sacroiliitis can predict acute inflammatory status of sacroiliac joint in early axial spondyloarthritis of male patients: a cross sectional study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019 Apr 4;20(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2549-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019. PMID: 30947732 Free PMC article.
-
Change in MRI in patients with spondyloarthritis treated with anti-TNF agents: systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2021 Mar-Apr;39(2):242-252. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/fsluso. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33506749
-
Effects of disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs on sacroiliac MRI score in axial spondyloarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Mar;43(3):1045-1052. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06849-5. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38158505
Cited by
-
Inflammatory activity evaluation in patients with axial spondyloarthritis using MRI relaxometry and mucosal-associated invariant T cells.Front Immunol. 2024 May 22;15:1391280. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1391280. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38840918 Free PMC article.
-
Increased serum levels of MIC1/GDF15 correlated with bone erosion in spondyloarthritis: A pilot study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Dec;97(51):e13733. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013733. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30572513 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors on MRI inflammation in axial spondyloarthritis assessed by Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium Canada score: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 31;15(12):e0244788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244788. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33382842 Free PMC article.
-
Interobserver Reliability of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Sacroiliac Joints in Axial Spondyloarthritis.Life (Basel). 2022 Mar 23;12(4):470. doi: 10.3390/life12040470. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454961 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of active inflammation, chronic structural damage, and response to treatment of sacroiliitis in axial spondyloarthritis using the Spondyloarthritis research consortium of Canada scoring system.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Jul 8;23(1):654. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05609-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 35804360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wigley RD, Zhang NZ, Zeng QY, Shi CS, Hu DW, Couchman K, et al. Rheumatic diseases in China: ILAR-China study comparing the prevalence of rheumatic symptoms in northern and southern rural populations. J Rheumatol. 1994;21:1484–1490. - PubMed
-
- Zhang NZ, Zeng QY, Zhang FS, Chen JB, Shi QS, Yao QP. An epidemiology study of rheumatic diseases in China. Chin J Rheumatol. 1997;1:31–35.
-
- Chen R, Wang QW, Lin QQ, Wu XR, Xu JC, Xie SH. Epidemiological study of spondyloarthropathies. Chin J Rheumatol. 2000;4:240–241.
-
- Chao TM, Han QW, Duan YC, Ji YB, Chen LZ, Dong DX. Epidemiological study of ankylosing spondylitis among some of the male soldiers stationed in the northeast military zone. Chin J Rheumatol. 2000;4:307–308.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

