Inborn Errors of Long-Chain Fatty Acid β-Oxidation Link Neural Stem Cell Self-Renewal to Autism
- PMID: 26832401
- PMCID: PMC4749429
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.01.004
Inborn Errors of Long-Chain Fatty Acid β-Oxidation Link Neural Stem Cell Self-Renewal to Autism
Abstract
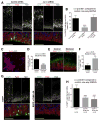
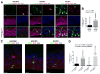
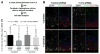
Inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs) occur with high incidence in human populations. Especially prevalent among these are inborn deficiencies in fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO), which are clinically associated with developmental neuropsychiatric disorders, including autism. We now report that neural stem cell (NSC)-autonomous insufficiencies in the activity of TMLHE (an autism risk factor that supports long-chain FAO by catalyzing carnitine biosynthesis), of CPT1A (an enzyme required for long-chain FAO transport into mitochondria), or of fatty acid mobilization from lipid droplets reduced NSC pools in the mouse embryonic neocortex. Lineage tracing experiments demonstrated that reduced flux through the FAO pathway potentiated NSC symmetric differentiating divisions at the expense of self-renewing stem cell division modes. The collective data reveal a key role for FAO in controlling NSC-to-IPC transition in the mammalian embryonic brain and suggest NSC self renewal as a cellular mechanism underlying the association between IEMs and autism.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bélanger M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ. Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab. 2011;14:724–738. - PubMed
-
- Bush KT, Lee H, Nagele RG. Lipid droplets of neuroepithelial cells are a major calcium storage site during neural tube formation in chick and mouse embryos. Experientia. 1992;48:516–519. - PubMed
-
- Clark-Taylor T, Clark-Taylor BE. Is autism a disorder of fatty acid metabolism? Possible dysfunction of mitochondrial beta-oxidation by long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Med Hypotheses. 2004;62:970–975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

