Caspase-1, but Not Caspase-3, Promotes Diabetic Nephropathy
- PMID: 26832955
- PMCID: PMC4978051
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015060676
Caspase-1, but Not Caspase-3, Promotes Diabetic Nephropathy
Abstract
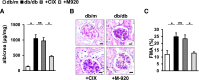
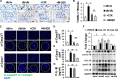
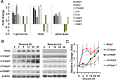
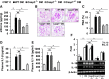
Glomerular apoptosis may contribute to diabetic nephropathy (dNP), but the pathophysiologic relevance of this process remains obscure. Here, we administered two partially disjunct polycaspase inhibitors in 8-week-old diabetic (db/db) mice: M-920 (inhibiting caspase-1, -3, -4, -5, -6, -7, and -8) and CIX (inhibiting caspase-3, -6, -7, -8, and -10). Notably, despite reduction in glomerular cell death and caspase-3 activity by both inhibitors, only M-920 ameliorated dNP. Nephroprotection by M-920 was associated with reduced renal caspase-1 and inflammasome activity. Accordingly, analysis of gene expression data in the Nephromine database revealed persistently elevated glomerular expression of inflammasome markers (NLRP3, CASP1, PYCARD, IL-18, IL-1β), but not of apoptosis markers (CASP3, CASP7, PARP1), in patients with and murine models of dNP. In vitro, increased levels of markers of inflammasome activation (Nlrp3, caspase-1 cleavage) preceded those of markers of apoptosis activation (caspase-3 and -7, PARP1 cleavage) in glucose-stressed podocytes. Finally, caspase-3 deficiency did not protect mice from dNP, whereas both homozygous and hemizygous caspase-1 deficiency did. Hence, these results suggest caspase-3-dependent cell death has a negligible effect, whereas caspase-1-dependent inflammasome activation has a crucial function in the establishment of dNP. Furthermore, small molecules targeting caspase-1 or inflammasome activation may be a feasible therapeutic approach in dNP.
Keywords: apoptosis; diabetic nephropathy; immunology; renal protection.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Susztak K, Raff AC, Schiffer M, Böttinger EP: Glucose-induced reactive oxygen species cause apoptosis of podocytes and podocyte depletion at the onset of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 55: 225–233, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Kumar D, Robertson S, Burns KD: Evidence of apoptosis in human diabetic kidney. Mol Cell Biochem 259: 67–70, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Shahzad K, Bock F, Dong W, Wang H, Kopf S, Kohli S, Al-Dabet MM, Ranjan S, Wolter J, Wacker C, Biemann R, Stoyanov S, Reymann K, Söderkvist P, Groß O, Schwenger V, Pahernik S, Nawroth PP, Gröne HJ, Madhusudhan T, Isermann B: Nlrp3-inflammasome activation in non-myeloid-derived cells aggravates diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 87: 74–84, 2015 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mudaliar H, Pollock C, Panchapakesan U: Role of Toll-like receptors in diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci (Lond) 126: 685–694, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Fischer U, Schulze-Osthoff K: Apoptosis-based therapies and drug targets. Cell Death Differ 12[Suppl 1]: 942–961, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

