Intestinal Phospholipid Remodeling Is Required for Dietary-Lipid Uptake and Survival on a High-Fat Diet
- PMID: 26833026
- PMCID: PMC4785086
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.01.001
Intestinal Phospholipid Remodeling Is Required for Dietary-Lipid Uptake and Survival on a High-Fat Diet
Abstract
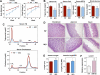
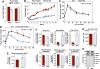
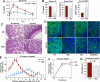
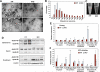
Phospholipids are important determinants of membrane biophysical properties, but the impact of membrane acyl chain composition on dietary-lipid absorption is unknown. Here we demonstrate that the LXR-responsive phospholipid-remodeling enzyme Lpcat3 modulates intestinal fatty acid and cholesterol absorption and is required for survival on a high-fat diet. Mice lacking Lpcat3 in the intestine thrive on carbohydrate-based chow but lose body weight rapidly and become moribund on a triglyceride-rich diet. Lpcat3-dependent incorporation of polyunsaturated fatty acids into phospholipids is required for the efficient transport of dietary lipids into enterocytes. Furthermore, loss of Lpcat3 amplifies the production of gut hormones, including GLP-1 and oleoylethanolamide, in response to high-fat feeding, contributing to the paradoxical cessation of food intake in the setting of starvation. These results reveal that membrane phospholipid composition is a gating factor in passive lipid absorption and implicate LXR-Lpcat3 signaling in a gut-brain feedback loop that couples absorption to food intake.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Begg DP, Woods SC. The endocrinology of food intake. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013;9:584–597. - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Yang Y, Braunstein E, Georgeson KE, Harmon CM. Gut expression and regulation of FAT/CD36: possible role in fatty acid transport in rat enterocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001;281:E916–923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL090553/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL074214/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL030568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL090553/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK099810/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM076516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103540/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM103540/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM076516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074214/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016042/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK041301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R24 DK099810/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL030568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

