Genome-wide meta-analysis uncovers novel loci influencing circulating leptin levels
- PMID: 26833098
- PMCID: PMC4740377
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10494
Genome-wide meta-analysis uncovers novel loci influencing circulating leptin levels
Abstract
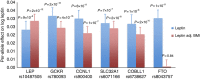
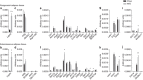
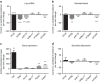
Leptin is an adipocyte-secreted hormone, the circulating levels of which correlate closely with overall adiposity. Although rare mutations in the leptin (LEP) gene are well known to cause leptin deficiency and severe obesity, no common loci regulating circulating leptin levels have been uncovered. Therefore, we performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of circulating leptin levels from 32,161 individuals and followed up loci reaching P<10(-6) in 19,979 additional individuals. We identify five loci robustly associated (P<5 × 10(-8)) with leptin levels in/near LEP, SLC32A1, GCKR, CCNL1 and FTO. Although the association of the FTO obesity locus with leptin levels is abolished by adjustment for BMI, associations of the four other loci are independent of adiposity. The GCKR locus was found associated with multiple metabolic traits in previous GWAS and the CCNL1 locus with birth weight. Knockdown experiments in mouse adipose tissue explants show convincing evidence for adipogenin, a regulator of adipocyte differentiation, as the novel causal gene in the SLC32A1 locus influencing leptin levels. Our findings provide novel insights into the regulation of leptin production by adipose tissue and open new avenues for examining the influence of variation in leptin levels on adiposity and metabolic health.
Conflict of interest statement
I.B. owns stock in GlaxoSmithKline and Incyte Corporation. F.M.F. has received honoraria, speaker fees or research funding from Astra Zeneca, Merck Sharp Dohme, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi. P.W. and G.W. received grants from GlaxoSmithKline, the Faculty of Biology and Medicine of Lausanne and the Swiss National Science Foundation (33CSCO-122661), to conduct the CoLaus study. A.A. is currently a consultant or a member of advisory board for Arena Pharmaceuticals Inc., USA; Basic Research, USA; BioCare Copenhagen, DK; Dutch Beer Knowledge Institute, NL; Gelesis, USA; Global Dairy Platform, USA; IKEA Food Scientific Health Advisory Board, SV; McCain Foods Ltd., USA; McDonald s, USA; Novo Nordisk, DK; Orexigen Therapeutics Inc., USA; S-Biotek, DK; and Weight Watchers, USA.
Figures

References
-
- Ahima R. S. et al. Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature 382, 250–252 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Montague C. T. et al. Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early-onset obesity in humans. Nature 387, 903–908 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Considine R. V. et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 334, 292–295 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA050385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00-HL-098459/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U147574242/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 1R01DK080015/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-24156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK075681/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- PG/13/66/30442/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01-HL-071252/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007033/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DK058845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071258/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088451/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 5R01DK068336/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA067262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N02 HL064278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071252/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MD009164/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL098459/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0701863/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL068891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 263 MD 821336/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- PG/07/131/24254/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL071250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK068336/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/J012165/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 1R01AG032098-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-088451/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT098017/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CA49449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062106/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA067262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK52431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA065725/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL117078/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075681/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CA67262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT089062/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071051/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL087700/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179472/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062103/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR-000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HL-043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 081917/Z/07/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DK-26687/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-25005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK089256/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089256/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080015/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 086596/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL071205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026687/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01AG62103/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071051/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA50385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 263MD9164/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR-001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117078/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12011/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-045670/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT064890/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 202802/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT091551/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087700/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_A620_1016/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC065226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA098233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071258/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- FRCN-CCT-83028/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- U01 HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN26800625226C/PHS HHS/United States
- U01-HG007033/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK07568102/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/8/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CA65725/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-65226/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL045670/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

