STK11/LKB1 Deficiency Promotes Neutrophil Recruitment and Proinflammatory Cytokine Production to Suppress T-cell Activity in the Lung Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 26833127
- PMCID: PMC4775354
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1439
STK11/LKB1 Deficiency Promotes Neutrophil Recruitment and Proinflammatory Cytokine Production to Suppress T-cell Activity in the Lung Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
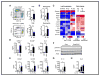
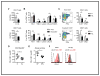
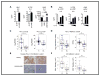
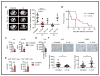
STK11/LKB1 is among the most commonly inactivated tumor suppressors in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), especially in tumors harboring KRAS mutations. Many oncogenes promote immune escape, undermining the effectiveness of immunotherapies, but it is unclear whether the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes, such as STK11/LKB1, exerts similar effects. In this study, we investigated the consequences of STK11/LKB1 loss on the immune microenvironment in a mouse model of KRAS-driven NSCLC. Genetic ablation of STK11/LKB1 resulted in accumulation of neutrophils with T-cell-suppressive effects, along with a corresponding increase in the expression of T-cell exhaustion markers and tumor-promoting cytokines. The number of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes was also reduced in LKB1-deficient mouse and human tumors. Furthermore, STK11/LKB1-inactivating mutations were associated with reduced expression of PD-1 ligand PD-L1 in mouse and patient tumors as well as in tumor-derived cell lines. Consistent with these results, PD-1-targeting antibodies were ineffective against Lkb1-deficient tumors. In contrast, treating Lkb1-deficient mice with an IL6-neutralizing antibody or a neutrophil-depleting antibody yielded therapeutic benefits associated with reduced neutrophil accumulation and proinflammatory cytokine expression. Our findings illustrate how tumor suppressor mutations can modulate the immune milieu of the tumor microenvironment, and they offer specific implications for addressing STK11/LKB1-mutated tumors with PD-1-targeting antibody therapies.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
G.D. received sponsored research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Novartis, and is currently an employee of Novartis. He is currently an employee of Novartis. G.J.F. receives patent royalties on the PD-1 pathway from Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Roche, Merck, EMD-Serrono, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Amplimmune/AstraZeneca, and Novartis. F.S.H. is a Bristol-Myers Squibb nonpaid consultant, Novartis, Merck and Genentech consultant and receives clinical trial support to the institution from these companies.
Figures
References
-
- Ji H, Ramsey MR, Hayes DN, Fan C, McNamara K, Kozlowski P, et al. LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. Nature. 2007;448(7155):807–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5R01CA163896-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA205150/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA166480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA195740-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01CA122794-10/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA070907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA195754/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA190394/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01CA140594-07/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA163896/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01CA166480-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI08995/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA195740/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

