Pathway-Specific Remodeling of Thalamostriatal Synapses in Parkinsonian Mice
- PMID: 26833136
- PMCID: PMC4760843
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.12.038
Pathway-Specific Remodeling of Thalamostriatal Synapses in Parkinsonian Mice
Abstract
Movement suppression in Parkinson's disease (PD) is thought to arise from increased efficacy of the indirect pathway basal ganglia circuit, relative to the direct pathway. However, the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms remain elusive. To examine whether changes in the strength of synaptic inputs to these circuits contribute to this imbalance, we obtained paired whole-cell recordings from striatal direct- and indirect-pathway medium spiny neurons (dMSNs and iMSNs) and optically stimulated inputs from sensorimotor cortex or intralaminar thalamus in brain slices from control and dopamine-depleted mice. We found that dopamine depletion selectively decreased synaptic strength at thalamic inputs to dMSNs, suggesting that thalamus drives asymmetric activation of basal ganglia circuitry underlying parkinsonian motor impairments. Consistent with this hypothesis, in vivo chemogenetic and optogenetic inhibition of thalamostriatal terminals reversed motor deficits in dopamine-depleted mice. These results implicate thalamostriatal projections in the pathophysiology of PD and support interventions targeting thalamus as a potential therapeutic strategy.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

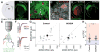
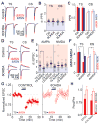

Comment in
-
Parkinson's Disease: A Thalamostriatal Rebalancing Act?Neuron. 2016 Feb 17;89(4):675-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.02.008. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 26889806 Free PMC article.
-
Are the basal ganglia actually controlling movement or quite the opposite?Mov Disord. 2016 Sep;31(9):1339. doi: 10.1002/mds.26680. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Mov Disord. 2016. PMID: 27270789 No abstract available.
References
-
- Caparros-Lefebvre D, Blond S, Feltin MP, Pollak P, Benabid AL. Improvement of levodopa induced dyskinesias by thalamic deep brain stimulation is related to slight variation in electrode placement: possible involvement of the centre median and parafascicularis complex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;67:308–314. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.67.3.308. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Day M, Wang Z, Ding J, An X, Ingham CA, Shering AF, Wokosin D, Ilijic E, Sun Z, Sampson AR, Mugnaini E, Deutch AY, Sesack SR, Arbuthnott GW, Surmeier DJ. Selective elimination of glutamatergic synapses on striatopallidal neurons in Parkinson disease models. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:251–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

