Doravirine Suppresses Common Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor-Associated Mutants at Clinically Relevant Concentrations
- PMID: 26833152
- PMCID: PMC4808216
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02650-15
Doravirine Suppresses Common Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor-Associated Mutants at Clinically Relevant Concentrations
Abstract
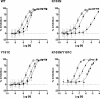
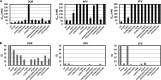
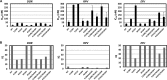
Doravirine (DOR), which is currently in a phase 3 clinical trial, is a novel human immunodeficiency type 1 virus (HIV-1) nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI). DOR exhibits potent antiviral activity against wild-type virus and K103N, Y181C, and K103N/Y181C mutant viruses, with 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) of 12, 21, 31, and 33 nM, respectively, when measured in 100% normal human serum (NHS). To assess the potential for DOR to suppress NNRTI-associated and rilpivirine (RPV)-specific mutants at concentrations achieved in the clinic setting, inhibitory quotients (IQs) were calculated by determining the ratio of the clinical trough concentration over the antiviral IC50for each virus with DOR and RPV and efavirenz (EFV). DOR displayed IQs of 39, 27, and 25 against the K103N, Y181C, and K103N/Y181C mutants, respectively. In contrast, RPV exhibited IQs of 4.6, 1.4, and 0.8, and EFV showed IQs of 2.5, 60, and 1.9 against these viruses, respectively. DOR also displayed higher IQs than those of RPV and EFV against other prevalent NNRTI-associated mutants, with the exception of Y188L. Both DOR and EFV exhibited higher IQs than RPV when analyzed with RPV-associated mutants. Resistance selections were conducted with K103N, Y181C, G190A, and K103N/Y181C mutants at clinically relevant concentrations of DOR, RPV, and EFV. No viral breakthrough was observed with DOR, whereas breakthrough viruses were readily detected with RPV and EFV against Y181C and K103N viruses, respectively. These data suggest that DOR should impose a higher barrier to the development of resistance than RPV and EFV at the concentrations achieved in the clinic setting.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Palella FJ Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, Aschman DJ, Holmberg SD. 1998. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Johnson JA, Li JF, Wei X, Lipscomb J, Irlbeck D, Craig C, Smith A, Bennett DE, Monsour M, Sandstrom P, Lanier ER, Heneine W. 2008. Minority HIV-1 drug resistance mutations are present in antiretroviral treatment-naive populations and associate with reduced treatment efficacy. PLoS Med 5:e158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050158. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pillay D, Bhaskaran K, Jurriaans S, Prins M, Masquelier B, Dabis F, Gifford R, Nielsen C, Pedersen C, Balotta C, Rezza G, Ortiz M, de Mendoza C, Kücherer C, Poggensee G, Gill J, Porter K, CASCADE Virology Collaboration . 2006. The impact of transmitted drug resistance on the natural history of HIV infection and response to first-line therapy. AIDS 20:21–28. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000196172.35056.b7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

