New loci for body fat percentage reveal link between adiposity and cardiometabolic disease risk
Affiliations
- 1 The Charles Bronfman Institute for Personalized Medicine, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- 2 The Department of Preventive Medicine, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- 3 MRC Epidemiology Unit, University of Cambridge School of Clinical Medicine, Institute of Metabolic Science, University of Cambridge, Cambridge Biomedical Campus, Cambridge CB2 0QQ, UK.
- 4 Science for Life Laboratory, Uppsala University, 750 85 Uppsala, Sweden.
- 5 Department of Medical Sciences, Molecular Epidemiology, Uppsala University, 751 85 Uppsala, Sweden.
- 6 Department of Genetics, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599, USA.
- 7 Department of Developmental and Regenerative Biology, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- 8 West Herts NHS Trust, Herts HP2 4AD, UK.
- 9 Department of Twin Research and Genetic Epidemiology, King's College London, London SE1 7EH, UK.
- 10 Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland, University of Helsinki, FI-00290 Helsinki, Finland.
- 11 Department Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Human Genetics, Lady Davis Institute, Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montréal, Quebec, Canada H3T1E2.
- 12 Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Oxford OX3 7BN, UK.
- 13 Estonian Genome Center, Univeristy of Tartu, Tartu, 51010, Estonia.
- 14 Broad Institute of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard University, Cambridge 2142, USA.
- 15 Divisions of Endocrinology and Genetics and Center for Basic and Translational Obesity Research, Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 16 Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 17 University of Queensland Diamantina Institute, Translational Research Institute, Brisbane, Queensland 4102, Australia.
- 18 MRC Integrative Epidemiology Unit, School of Social and Community Medicine, University of Bristol, Bristol BS82BN, UKnited.
- 19 Department of Genomics of Common Disease, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, London W12 0NN, UK.
- 20 Division of Statistical Genomics, Department of Genetics, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, Missouri 63108, USA.
- 21 Institute of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, University Medicine Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 22 European University of Applied Sciences, Faculty of Applied Public Health, 18055 Rostock, Germany.
- 23 Leeds Institute of Cancer and Pathology, Cancer Research UK Leeds Centre, University of Leeds, Leeds LS9 7TF, UK.
- 24 Department of Epidemiology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599, USA.
- 25 William Harvey Research Institute, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry, Queen Mary University of London, London EC1M 6BQ, UK.
- 26 Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Human Genetics, Hinxton, Cambridge CB10 1SA, UK.
- 27 Oxford Centre for Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism, University of Oxford, Churchill Hospital, Oxford OX3 7LJ, UK.
- 28 Department of Epidemiology, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 29 Center for Statistical Genetics, Department of Biostatistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 30 Department of Biostatistics, Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts 02118, USA.
- 31 Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research, Section of Metabolic Genetics, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 32 Medical and Population Genetics Program, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge 02142, USA.
- 33 Department of Epidemiology Research, Statens Serum Institut, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 34 Department of Epidemiology and Popualtion Health, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York 10461, USA.
- 35 Department of Computational Medicine and Bioinformatics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 36 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Imperial College London, London W2 1PG, UK.
- 37 Ealing Hospital NHS Trust, Middlesex UB1 3HW, UK.
- 38 Lund University Diabetes Centre, Department of Clinical Science, Genetic and Molecular Epidemiology Unit, Skåne University Hosptial, 205 02 Malmö, Sweden.
- 39 Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine, Unit of Medicine, Umeå University, 901 87 Umeå, Sweden.
- 40 Department of Odontology, Umeå University, 901 85 Umeå, Sweden.
- 41 Institute for Community Medicine, University Medicine Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 42 Interfaculty Institute for Genetics and Functional Genomics, University Medicine Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 43 Queensland Brain Institute, The University of Queensland, Brisbane 4072, Australia.
- 44 Program in Medical and Population Genetics, Broad Institute of Harvard and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142, USA.
- 45 Divisions of Genetics and Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02446, USA.
- 46 Partners Center for Personalized Genetic Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02446, USA.
- 47 Department of Dermatology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 48 Copenhagen Prospective Studies on Asthma in Childhood, Faculty of Health and Medical Sceinces, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 49 Danish Pediatric Asthma Center, Gentofte Hospital, The Capital Region, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 50 Steno Diabetes Center A/S, DK-2820 Gentofte, Denmark.
- 51 University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Department of Medicine, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 52 Department of Genetics, Texas Biomedical Research Institute, San Antonio, Texas 78245, USA.
- 53 CNRS UMR 8199, F-59019 Lille, France.
- 54 European Genomic Institute for Diabetes, 59000 Lille, France.
- 55 Université de Lille 2, 59000 Lille, France.
- 56 National Institute for Health and Welfare, FI-00271 Helsinki, Finland.
- 57 Rush Alzheimer's Disease Center, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, Illinois 60612, USA.
- 58 Department of Public Health and Caring Sciences, Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism, Uppsala University, 751 85 Uppsala, Sweden.
- 59 Lifespan Health Research Center, Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine, Dayton, Ohio 45420, USA.
- 60 Department of Anatomy, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea.
- 61 South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, Brownsville, Texas 78520.
- 62 Department of Human Nutrition, Wageningen University, 6700 EV Wageningen, The Netherlands.
- 63 Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 64 Program in Translational NeuroPsychiatric Genomics, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 65 Department of Internal Medicine, Erasmus Medical Center, 3015GE Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- 66 California Pacific Medical Center Research Institute, San Francisco, California 94107, USA.
- 67 Department of General Practice and Primary Health Care, University of Helsinki, FI-00014 Helsinki, Finland.
- 68 INSERM, UMR_S 1138, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, F-75006 Paris, France.
- 69 Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ Paris 06, UMR_S 1138, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, F-75006 Paris, France.
- 70 Université Paris Descartes, Sorbonne Paris Cité, UMR_S 1138, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, F-75006 Paris, France.
- 71 Univ Paris Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, UMR_S 1138, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, F-75006 Paris, France.
- 72 Laboratory of Epidemiology and Population Sciences, National Institute on Aging, Bethesda, Maryland 20892, USA.
- 73 Department of Medicine A, University Medicine Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 74 Center for Genome Science, National Institute of Health, Osong Health Technology Administration Complex, Chungcheongbuk-do 370914, Korea.
- 75 MRC Human Genetics Unit, Institute of Genetics and Molecular Medicine, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh EH4 2XU, UK.
- 76 Laboratory of Neurogenetics, National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland 20892, USA.
- 77 University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Department of Cardiology, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 78 Department of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, University of Split, Split 21000, Croatia.
- 79 Hospital District of North Karelia, FI-80210 Joensuu, Finland.
- 80 Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, University of Eastern Finland, FI-70211 Kuopio, Finland.
- 81 Folkhälsan Research Centre, FI-00290 Helsinki, Finland.
- 82 Institute of Behavioural Sciences, University of Helsinki, FI-00014 Helsinki, Finland.
- 83 Department of Medicine, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon 97239, USA.
- 84 Research Service, Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Portland, Oregon 97239, USA.
- 85 Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics, Department of Vertebrate Genomics, 14195 Berlin, Germany.
- 86 Max Planck Institute for Human Development, 14194 Berlin, Germany.
- 87 Thurston Arthritis Research Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chaper Hill, North Carolina 27599-7280, USA.
- 88 Translational Laboratory in Genetic Medicine (TLGM), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), 8A Biomedical Grove, Immunos, Level 5, Singapore 138648, Singapore.
- 89 Department of Clinical Chemistry, University of Tampere School of Medicine, FI-33014 Tampere, Finland.
- 90 Department of Clinical Chemistry, Fimlab Laboratories and School of Medicine, University of Tampere, FI-33520 Tampere, Finland.
- 91 Netherlands Genomics Initiative (NGI)-sponsored Netherlands Consortium for Healthy Aging (NCHA), Rotterdam The Netherlands.
- 92 Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus Medical Center, 3015GE Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- 93 Department of Surgical Sciences, Orthopedics, Uppsala University, 751 85 Uppsala, Sweden.
- 94 School of Public Health, Oregon Health &Science University, Portland, Oregon 97239, USA.
- 95 Bone &Mineral Unit, Oregon Health &Science University, Portland, Oregon 97239, USA.
- 96 Institute of Cell &Molecular Biosciences, Newcastle University, Newcastle NE1 7RU, UK.
- 97 Centre for Global Health Research, Usher Institute of Population Health Sciences and Informatics, University of Edinburgh, Teviot Place, Edinburgh EH8 9AG, UK.
- 98 Hjelt Institute, University of Helsinki, FI-00014 Helsinki, Finland.
- 99 Human Genomics Laboratory, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, Los Angeles 70808, USA.
- 100 Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea.
- 101 Institute for Anthropological Research, Zagreb 10000, Croatia.
- 102 The Berlin Aging Study II; Research Group on Geriatrics; Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, 13347 Berlin, Germany.
- 103 Lipid Clinic at the Interdisciplinary Metabolism Center, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, 13353 Berlin, Germany.
- 104 Division of Biostatistics, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, Missouri 63110, USA.
- 105 EMGO Institute for Health and Care Research, VU University Medical Center, 1081 BT Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 106 VUMC, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, 1081 BT Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 107 Department of Pediatrics, University of Oulu, FI-90014 Oulu, Finland.
- 108 Department of Pediatrics, Vaasa Central Hospital, FI-65100 Vaasa, Finland.
- 109 Translational Gerontology Branch, National Institute on Aging, Baltimore, Maryland 21225, USA.
- 110 Department of Epidemiology; University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15261, USA.
- 111 Tropical Metabolism Research Unit, Tropical Medicine Research Institute, University of the West Indies, Mona JMAAW15, Jamaica.
- 112 Faculty of Health Sciences, Institute of Clinical Medicine, Internal Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, 70210 Kuopio, Finland.
- 113 Department of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, 70210 Kuopio, Finland.
- 114 Kuopio University Hospital, 70029 Kuopio, Finland.
- 115 Institute of Human Genetics, Helmholtz Zentrum München-German Research Center for Environmental Health, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 116 Institute of Genetic Epidemiology, Helmholtz Zentrum München-German Research Center for Environmental Health, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 117 Department of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital, 70210 Kuopio, Finland.
- 118 Genetic Epidemiology Unit, Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus University Medical Center, 3015GE Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- 119 Institute of Epidemiology I, Helmholtz Zentrum München-German Research Center for Environmental Health, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 120 Institute of Epidemiology II, Helmholtz Zentrum München-German Research Center for Environmental Health, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 121 Icelandic Heart Association, Kopavogur 201, Iceland.
- 122 University of Iceland, Faculty of Medicine, Reykjavik 101, Iceland.
- 123 Department of Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115.
- 124 Institute for Aging Research Hebrew Senior Life, Boston, Massachusetts 02131, USA.
- 125 Research Unit of Molecular Epidemiology, Helmholtz Zentrum München-German Research Center for Environmental Health, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 126 Cardiovascular Health Research Unit, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98101, USA.
- 127 Program in Biostatistics and Biomathematics, Divison of Public Health Sciences, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, Washington 98109, USA.
- 128 Department of Biostatistics, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195, USA.
- 129 Program for Personalized and Genomic Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Nutrition, Department of Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland 21201, USA.
- 130 Geriatric Research and Education Clinical Center, Vetrans Administration Medical Center, Baltimore, Maryland 21042, USA.
- 131 Genetics, Projects Clinical Platforms and Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19112, USA.
- 132 Centre for Bone and Arthritis Research, Department of Internal Medicine and Clinical Nutrition, Institute of Medicine, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, 413 45 Gothenburg, Sweden.
- 133 Center for Medical Systems Biology, 2300 Leiden, The Netherlands.
- 134 Department of Internal Medicine, University Hospital Lausanne (CHUV) and University of Lausanne, 1011 Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 135 University of Leipzig, IFB Adiposity Diseases, 04103 Leipzig, Germany.
- 136 University of Leipzig, Department of Medicine, 04103 Leipzig, Germany.
- 137 Department of Public Health Sciences, Stritch School of Medicine, Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Illinois 61053, USA.
- 138 German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 139 Institute of Cardiovascular Science, University College London, London WC1E 6BT, UK.
- 140 Department of Clinical Medicine, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 141 Faculty of Medicine, University of Aalborg, 9220 Aalborg, Denmark.
- 142 Research Centre for Prevention and Health, DK2600 Capital Region of Denmark, Denmark.
- 143 Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, UCL, London WC1E 6BT, UK.
- 144 Research Centre for Prevention and Health, Glostrup Hospital, 2600 Glostrup, Denmark.
- 145 Massachusetts General Hospital, Center for Human Genetic Research, Psychiatric and Neurodevelopmental Genetics Unit, Boston, Massachusetts 02114, USA.
- 146 Institute of Medical Informatics, Biometry and Epidemiology, Chair of Genetic Epidemiology, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, 81377 Munich, Germany.
- 147 School of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College London, London W6 8RP, UK.
- 148 Lübeck Interdisciplinary Platform for Genome Analytics, Institutes of Neurogenetics and Integrative and Experimental Genomics, University of Lübeck, 23562 Lübeck, Germany.
- 149 Ajou University School of Medicine, Department of Preventive Medicine, Suwon Kyoung-gi 443-721, Korea.
- 150 Institute of Medical and Human Genetics, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, 13353 Berlin, Germany.
- 151 Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Southern Denmark, 5000 Odense, Denmark.
- 152 Department of Clinical Physiology, Tampere University Hospital, FI-33521 Tampere, Finland.
- 153 Department of Clinical Physiology, University of Tampere School of Medicine, FI-33014 Tampere, Finland.
- 154 Children's Hospital, Helsinki University Hospital and University of Helsinki, FI-00029 Helsinki, Finland.
- 155 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, MRC Oulu, Oulu University Hospital and University of Oulu, FI-90029 Oulu, Finland.
- 156 Department of Medical Sciences, Uppsala University, 751 85 Uppsala, Sweden.
- 157 Center for Human Genetics, Division of Public Health Sciences, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina 27157, USA.
- 158 MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Unit, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, Southampton SO16 6YD, UK.
- 159 Department of Kinesiology, Laval University, Québec City, Quebec, Canada G1V 0A6.
- 160 Institute of Nutrition and Functional Foods, Laval University, Québec City, Quebec, Canada G1V 0A6.
- 161 Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine, Turku University Hospital, FI-20521 Turku, Finland.
- 162 Research Centre of Applied and Preventive Cardiovascular Medicine, University of Turku, FI-20520 Turku, Finland.
- 163 Department of Psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, Missouri 63110, USA.
- 164 Institute of Preventive Medicine, Bispebjerg and Frederiksberg Hospital, The Capital Region, 2000 Frederiksberg, Denmark.
- 165 Durrer Center for Cardiogenetic Research, Interuniversity Cardiology Institute Netherlands-Netherlands Heart Institute, 3501 DG Utrecht, The Netherlands.
- 166 Department of Genetics, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 167 Department of Medicine, University of Turku, FI-20521 Turku, Finland.
- 168 School of Nutrition, Laval University, Québec City, Quebec, Canada G1V 0A6.
- 169 DZHK (German Centre for Cardiovascular Research), partner site Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 170 DZD (German Centre for Diabetes Research), partner site Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 171 Institute of Cellular Medicine, Newcastle University, Newcastle NE2 4HH, UK.
- 172 Centre for Population Health Sciences, Usher Institute of Population Health Sciences and Informatics, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh EH8 9AG, UK.
- 173 Analytical Genetics Group, Regeneron Genetics Center, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Tarrytown, New York 10591, USA.
- 174 Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London W12 0HS, UK.
- 175 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the Framingham Heart Study, Framingham, Massachusetts 01702, USA.
- 176 Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus Medical Center, 3000CA Rotterdam/Zuidholland, The Netherlands.
- 177 Princess Al-Jawhara Al-Brahim Centre of Excellence in Research of Hereditary Disorders (PACER-HD), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah 21589, Saudi Arabia.
- 178 Department of Biology, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599, USA.
- 179 Department of Epidemiology, Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health, Melvin and Bren Simon Cancer Center, Indianapolis, Indiana 46202, USA.
- 180 Channing Division of Network Medicine, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 181 Department of Nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 182 Oxford NIHR Biomedical Research Centre, Oxford OX3 7LJ, UK.
- 183 National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College London, London W12 0NN, UK.
- 184 Boston University School of Medicine, Department of Medicine, Section of General Internal Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118, USA.
- 185 NHLBI's and Boston University's Framingham Heart Study, Framingham, Massachusetts 01702, USA.
- 186 Department of Biostatistics, University of Liverpool, Liverpool L69 3GA, UK.
- 187 Carolina Center for Genome Sciences and Department of Epidemiology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599-7400, USA.
- 188 MRC Unit for Lifelong Health and Ageing at UCL, London WC1B 5JU, UK.
- 189 Department of Paediatrics, University of Cambridge, Cambridge CB2 0QQ, UK.
- 190 Department of Medicine, Lady Davis Institute, Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montréal, Quebec, Canada H3T1E2.
- 191 Department of Twin Research, King's College London, London SE1 1E7, UK.
- 192 Division of Endocrinology, Lady Davis Institute, Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montréal, Quebec, Canada H3T1E2.
- 193 Icahn Institute for Genomics and Multiscale Biology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- 194 Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- 195 Department of Human Genetics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 196 Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 197 Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California 94305, USA.
- 198 Department of Epigenetics, Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics, D-76108 Freiburg, Germany.
- 199 The Big Data Institute, University of Oxford, Oxford OX3 7LJ, UK.
- 200 The Genetics of Obesity and Related Metabolic Traits Program, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York, 10029, USA.
- 201 The Mindich Child Health and Development Institute, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- PMID: 26833246
- PMCID: PMC4740398
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10495
New loci for body fat percentage reveal link between adiposity and cardiometabolic disease risk
Authors
Affiliations
- 1 The Charles Bronfman Institute for Personalized Medicine, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- 2 The Department of Preventive Medicine, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- 3 MRC Epidemiology Unit, University of Cambridge School of Clinical Medicine, Institute of Metabolic Science, University of Cambridge, Cambridge Biomedical Campus, Cambridge CB2 0QQ, UK.
- 4 Science for Life Laboratory, Uppsala University, 750 85 Uppsala, Sweden.
- 5 Department of Medical Sciences, Molecular Epidemiology, Uppsala University, 751 85 Uppsala, Sweden.
- 6 Department of Genetics, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599, USA.
- 7 Department of Developmental and Regenerative Biology, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- 8 West Herts NHS Trust, Herts HP2 4AD, UK.
- 9 Department of Twin Research and Genetic Epidemiology, King's College London, London SE1 7EH, UK.
- 10 Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland, University of Helsinki, FI-00290 Helsinki, Finland.
- 11 Department Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Human Genetics, Lady Davis Institute, Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montréal, Quebec, Canada H3T1E2.
- 12 Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Oxford OX3 7BN, UK.
- 13 Estonian Genome Center, Univeristy of Tartu, Tartu, 51010, Estonia.
- 14 Broad Institute of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard University, Cambridge 2142, USA.
- 15 Divisions of Endocrinology and Genetics and Center for Basic and Translational Obesity Research, Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 16 Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 17 University of Queensland Diamantina Institute, Translational Research Institute, Brisbane, Queensland 4102, Australia.
- 18 MRC Integrative Epidemiology Unit, School of Social and Community Medicine, University of Bristol, Bristol BS82BN, UKnited.
- 19 Department of Genomics of Common Disease, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, London W12 0NN, UK.
- 20 Division of Statistical Genomics, Department of Genetics, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, Missouri 63108, USA.
- 21 Institute of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, University Medicine Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 22 European University of Applied Sciences, Faculty of Applied Public Health, 18055 Rostock, Germany.
- 23 Leeds Institute of Cancer and Pathology, Cancer Research UK Leeds Centre, University of Leeds, Leeds LS9 7TF, UK.
- 24 Department of Epidemiology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599, USA.
- 25 William Harvey Research Institute, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry, Queen Mary University of London, London EC1M 6BQ, UK.
- 26 Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Human Genetics, Hinxton, Cambridge CB10 1SA, UK.
- 27 Oxford Centre for Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism, University of Oxford, Churchill Hospital, Oxford OX3 7LJ, UK.
- 28 Department of Epidemiology, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 29 Center for Statistical Genetics, Department of Biostatistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 30 Department of Biostatistics, Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts 02118, USA.
- 31 Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research, Section of Metabolic Genetics, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 32 Medical and Population Genetics Program, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge 02142, USA.
- 33 Department of Epidemiology Research, Statens Serum Institut, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 34 Department of Epidemiology and Popualtion Health, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York 10461, USA.
- 35 Department of Computational Medicine and Bioinformatics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 36 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Imperial College London, London W2 1PG, UK.
- 37 Ealing Hospital NHS Trust, Middlesex UB1 3HW, UK.
- 38 Lund University Diabetes Centre, Department of Clinical Science, Genetic and Molecular Epidemiology Unit, Skåne University Hosptial, 205 02 Malmö, Sweden.
- 39 Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine, Unit of Medicine, Umeå University, 901 87 Umeå, Sweden.
- 40 Department of Odontology, Umeå University, 901 85 Umeå, Sweden.
- 41 Institute for Community Medicine, University Medicine Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 42 Interfaculty Institute for Genetics and Functional Genomics, University Medicine Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 43 Queensland Brain Institute, The University of Queensland, Brisbane 4072, Australia.
- 44 Program in Medical and Population Genetics, Broad Institute of Harvard and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142, USA.
- 45 Divisions of Genetics and Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02446, USA.
- 46 Partners Center for Personalized Genetic Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02446, USA.
- 47 Department of Dermatology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 48 Copenhagen Prospective Studies on Asthma in Childhood, Faculty of Health and Medical Sceinces, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 49 Danish Pediatric Asthma Center, Gentofte Hospital, The Capital Region, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 50 Steno Diabetes Center A/S, DK-2820 Gentofte, Denmark.
- 51 University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Department of Medicine, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 52 Department of Genetics, Texas Biomedical Research Institute, San Antonio, Texas 78245, USA.
- 53 CNRS UMR 8199, F-59019 Lille, France.
- 54 European Genomic Institute for Diabetes, 59000 Lille, France.
- 55 Université de Lille 2, 59000 Lille, France.
- 56 National Institute for Health and Welfare, FI-00271 Helsinki, Finland.
- 57 Rush Alzheimer's Disease Center, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, Illinois 60612, USA.
- 58 Department of Public Health and Caring Sciences, Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism, Uppsala University, 751 85 Uppsala, Sweden.
- 59 Lifespan Health Research Center, Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine, Dayton, Ohio 45420, USA.
- 60 Department of Anatomy, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea.
- 61 South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, Brownsville, Texas 78520.
- 62 Department of Human Nutrition, Wageningen University, 6700 EV Wageningen, The Netherlands.
- 63 Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 64 Program in Translational NeuroPsychiatric Genomics, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 65 Department of Internal Medicine, Erasmus Medical Center, 3015GE Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- 66 California Pacific Medical Center Research Institute, San Francisco, California 94107, USA.
- 67 Department of General Practice and Primary Health Care, University of Helsinki, FI-00014 Helsinki, Finland.
- 68 INSERM, UMR_S 1138, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, F-75006 Paris, France.
- 69 Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ Paris 06, UMR_S 1138, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, F-75006 Paris, France.
- 70 Université Paris Descartes, Sorbonne Paris Cité, UMR_S 1138, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, F-75006 Paris, France.
- 71 Univ Paris Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, UMR_S 1138, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, F-75006 Paris, France.
- 72 Laboratory of Epidemiology and Population Sciences, National Institute on Aging, Bethesda, Maryland 20892, USA.
- 73 Department of Medicine A, University Medicine Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 74 Center for Genome Science, National Institute of Health, Osong Health Technology Administration Complex, Chungcheongbuk-do 370914, Korea.
- 75 MRC Human Genetics Unit, Institute of Genetics and Molecular Medicine, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh EH4 2XU, UK.
- 76 Laboratory of Neurogenetics, National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland 20892, USA.
- 77 University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Department of Cardiology, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 78 Department of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, University of Split, Split 21000, Croatia.
- 79 Hospital District of North Karelia, FI-80210 Joensuu, Finland.
- 80 Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, University of Eastern Finland, FI-70211 Kuopio, Finland.
- 81 Folkhälsan Research Centre, FI-00290 Helsinki, Finland.
- 82 Institute of Behavioural Sciences, University of Helsinki, FI-00014 Helsinki, Finland.
- 83 Department of Medicine, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon 97239, USA.
- 84 Research Service, Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Portland, Oregon 97239, USA.
- 85 Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics, Department of Vertebrate Genomics, 14195 Berlin, Germany.
- 86 Max Planck Institute for Human Development, 14194 Berlin, Germany.
- 87 Thurston Arthritis Research Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chaper Hill, North Carolina 27599-7280, USA.
- 88 Translational Laboratory in Genetic Medicine (TLGM), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), 8A Biomedical Grove, Immunos, Level 5, Singapore 138648, Singapore.
- 89 Department of Clinical Chemistry, University of Tampere School of Medicine, FI-33014 Tampere, Finland.
- 90 Department of Clinical Chemistry, Fimlab Laboratories and School of Medicine, University of Tampere, FI-33520 Tampere, Finland.
- 91 Netherlands Genomics Initiative (NGI)-sponsored Netherlands Consortium for Healthy Aging (NCHA), Rotterdam The Netherlands.
- 92 Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus Medical Center, 3015GE Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- 93 Department of Surgical Sciences, Orthopedics, Uppsala University, 751 85 Uppsala, Sweden.
- 94 School of Public Health, Oregon Health &Science University, Portland, Oregon 97239, USA.
- 95 Bone &Mineral Unit, Oregon Health &Science University, Portland, Oregon 97239, USA.
- 96 Institute of Cell &Molecular Biosciences, Newcastle University, Newcastle NE1 7RU, UK.
- 97 Centre for Global Health Research, Usher Institute of Population Health Sciences and Informatics, University of Edinburgh, Teviot Place, Edinburgh EH8 9AG, UK.
- 98 Hjelt Institute, University of Helsinki, FI-00014 Helsinki, Finland.
- 99 Human Genomics Laboratory, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, Los Angeles 70808, USA.
- 100 Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea.
- 101 Institute for Anthropological Research, Zagreb 10000, Croatia.
- 102 The Berlin Aging Study II; Research Group on Geriatrics; Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, 13347 Berlin, Germany.
- 103 Lipid Clinic at the Interdisciplinary Metabolism Center, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, 13353 Berlin, Germany.
- 104 Division of Biostatistics, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, Missouri 63110, USA.
- 105 EMGO Institute for Health and Care Research, VU University Medical Center, 1081 BT Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 106 VUMC, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, 1081 BT Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 107 Department of Pediatrics, University of Oulu, FI-90014 Oulu, Finland.
- 108 Department of Pediatrics, Vaasa Central Hospital, FI-65100 Vaasa, Finland.
- 109 Translational Gerontology Branch, National Institute on Aging, Baltimore, Maryland 21225, USA.
- 110 Department of Epidemiology; University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15261, USA.
- 111 Tropical Metabolism Research Unit, Tropical Medicine Research Institute, University of the West Indies, Mona JMAAW15, Jamaica.
- 112 Faculty of Health Sciences, Institute of Clinical Medicine, Internal Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, 70210 Kuopio, Finland.
- 113 Department of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, 70210 Kuopio, Finland.
- 114 Kuopio University Hospital, 70029 Kuopio, Finland.
- 115 Institute of Human Genetics, Helmholtz Zentrum München-German Research Center for Environmental Health, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 116 Institute of Genetic Epidemiology, Helmholtz Zentrum München-German Research Center for Environmental Health, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 117 Department of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital, 70210 Kuopio, Finland.
- 118 Genetic Epidemiology Unit, Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus University Medical Center, 3015GE Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- 119 Institute of Epidemiology I, Helmholtz Zentrum München-German Research Center for Environmental Health, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 120 Institute of Epidemiology II, Helmholtz Zentrum München-German Research Center for Environmental Health, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 121 Icelandic Heart Association, Kopavogur 201, Iceland.
- 122 University of Iceland, Faculty of Medicine, Reykjavik 101, Iceland.
- 123 Department of Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115.
- 124 Institute for Aging Research Hebrew Senior Life, Boston, Massachusetts 02131, USA.
- 125 Research Unit of Molecular Epidemiology, Helmholtz Zentrum München-German Research Center for Environmental Health, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 126 Cardiovascular Health Research Unit, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98101, USA.
- 127 Program in Biostatistics and Biomathematics, Divison of Public Health Sciences, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, Washington 98109, USA.
- 128 Department of Biostatistics, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195, USA.
- 129 Program for Personalized and Genomic Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Nutrition, Department of Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland 21201, USA.
- 130 Geriatric Research and Education Clinical Center, Vetrans Administration Medical Center, Baltimore, Maryland 21042, USA.
- 131 Genetics, Projects Clinical Platforms and Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19112, USA.
- 132 Centre for Bone and Arthritis Research, Department of Internal Medicine and Clinical Nutrition, Institute of Medicine, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, 413 45 Gothenburg, Sweden.
- 133 Center for Medical Systems Biology, 2300 Leiden, The Netherlands.
- 134 Department of Internal Medicine, University Hospital Lausanne (CHUV) and University of Lausanne, 1011 Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 135 University of Leipzig, IFB Adiposity Diseases, 04103 Leipzig, Germany.
- 136 University of Leipzig, Department of Medicine, 04103 Leipzig, Germany.
- 137 Department of Public Health Sciences, Stritch School of Medicine, Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Illinois 61053, USA.
- 138 German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), 85764 Neuherberg, Germany.
- 139 Institute of Cardiovascular Science, University College London, London WC1E 6BT, UK.
- 140 Department of Clinical Medicine, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 141 Faculty of Medicine, University of Aalborg, 9220 Aalborg, Denmark.
- 142 Research Centre for Prevention and Health, DK2600 Capital Region of Denmark, Denmark.
- 143 Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, UCL, London WC1E 6BT, UK.
- 144 Research Centre for Prevention and Health, Glostrup Hospital, 2600 Glostrup, Denmark.
- 145 Massachusetts General Hospital, Center for Human Genetic Research, Psychiatric and Neurodevelopmental Genetics Unit, Boston, Massachusetts 02114, USA.
- 146 Institute of Medical Informatics, Biometry and Epidemiology, Chair of Genetic Epidemiology, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, 81377 Munich, Germany.
- 147 School of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College London, London W6 8RP, UK.
- 148 Lübeck Interdisciplinary Platform for Genome Analytics, Institutes of Neurogenetics and Integrative and Experimental Genomics, University of Lübeck, 23562 Lübeck, Germany.
- 149 Ajou University School of Medicine, Department of Preventive Medicine, Suwon Kyoung-gi 443-721, Korea.
- 150 Institute of Medical and Human Genetics, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, 13353 Berlin, Germany.
- 151 Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Southern Denmark, 5000 Odense, Denmark.
- 152 Department of Clinical Physiology, Tampere University Hospital, FI-33521 Tampere, Finland.
- 153 Department of Clinical Physiology, University of Tampere School of Medicine, FI-33014 Tampere, Finland.
- 154 Children's Hospital, Helsinki University Hospital and University of Helsinki, FI-00029 Helsinki, Finland.
- 155 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, MRC Oulu, Oulu University Hospital and University of Oulu, FI-90029 Oulu, Finland.
- 156 Department of Medical Sciences, Uppsala University, 751 85 Uppsala, Sweden.
- 157 Center for Human Genetics, Division of Public Health Sciences, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina 27157, USA.
- 158 MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Unit, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, Southampton SO16 6YD, UK.
- 159 Department of Kinesiology, Laval University, Québec City, Quebec, Canada G1V 0A6.
- 160 Institute of Nutrition and Functional Foods, Laval University, Québec City, Quebec, Canada G1V 0A6.
- 161 Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine, Turku University Hospital, FI-20521 Turku, Finland.
- 162 Research Centre of Applied and Preventive Cardiovascular Medicine, University of Turku, FI-20520 Turku, Finland.
- 163 Department of Psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, Missouri 63110, USA.
- 164 Institute of Preventive Medicine, Bispebjerg and Frederiksberg Hospital, The Capital Region, 2000 Frederiksberg, Denmark.
- 165 Durrer Center for Cardiogenetic Research, Interuniversity Cardiology Institute Netherlands-Netherlands Heart Institute, 3501 DG Utrecht, The Netherlands.
- 166 Department of Genetics, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 167 Department of Medicine, University of Turku, FI-20521 Turku, Finland.
- 168 School of Nutrition, Laval University, Québec City, Quebec, Canada G1V 0A6.
- 169 DZHK (German Centre for Cardiovascular Research), partner site Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 170 DZD (German Centre for Diabetes Research), partner site Greifswald, 17475 Greifswald, Germany.
- 171 Institute of Cellular Medicine, Newcastle University, Newcastle NE2 4HH, UK.
- 172 Centre for Population Health Sciences, Usher Institute of Population Health Sciences and Informatics, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh EH8 9AG, UK.
- 173 Analytical Genetics Group, Regeneron Genetics Center, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Tarrytown, New York 10591, USA.
- 174 Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London W12 0HS, UK.
- 175 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the Framingham Heart Study, Framingham, Massachusetts 01702, USA.
- 176 Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus Medical Center, 3000CA Rotterdam/Zuidholland, The Netherlands.
- 177 Princess Al-Jawhara Al-Brahim Centre of Excellence in Research of Hereditary Disorders (PACER-HD), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah 21589, Saudi Arabia.
- 178 Department of Biology, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599, USA.
- 179 Department of Epidemiology, Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health, Melvin and Bren Simon Cancer Center, Indianapolis, Indiana 46202, USA.
- 180 Channing Division of Network Medicine, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 181 Department of Nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 182 Oxford NIHR Biomedical Research Centre, Oxford OX3 7LJ, UK.
- 183 National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College London, London W12 0NN, UK.
- 184 Boston University School of Medicine, Department of Medicine, Section of General Internal Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118, USA.
- 185 NHLBI's and Boston University's Framingham Heart Study, Framingham, Massachusetts 01702, USA.
- 186 Department of Biostatistics, University of Liverpool, Liverpool L69 3GA, UK.
- 187 Carolina Center for Genome Sciences and Department of Epidemiology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599-7400, USA.
- 188 MRC Unit for Lifelong Health and Ageing at UCL, London WC1B 5JU, UK.
- 189 Department of Paediatrics, University of Cambridge, Cambridge CB2 0QQ, UK.
- 190 Department of Medicine, Lady Davis Institute, Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montréal, Quebec, Canada H3T1E2.
- 191 Department of Twin Research, King's College London, London SE1 1E7, UK.
- 192 Division of Endocrinology, Lady Davis Institute, Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montréal, Quebec, Canada H3T1E2.
- 193 Icahn Institute for Genomics and Multiscale Biology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- 194 Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- 195 Department of Human Genetics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 196 Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 197 Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California 94305, USA.
- 198 Department of Epigenetics, Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics, D-76108 Freiburg, Germany.
- 199 The Big Data Institute, University of Oxford, Oxford OX3 7LJ, UK.
- 200 The Genetics of Obesity and Related Metabolic Traits Program, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York, 10029, USA.
- 201 The Mindich Child Health and Development Institute, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York 10029, USA.
- PMID: 26833246
- PMCID: PMC4740398
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10495
Abstract
To increase our understanding of the genetic basis of adiposity and its links to cardiometabolic disease risk, we conducted a genome-wide association meta-analysis of body fat percentage (BF%) in up to 100,716 individuals. Twelve loci reached genome-wide significance (P<5 × 10(-8)), of which eight were previously associated with increased overall adiposity (BMI, BF%) and four (in or near COBLL1/GRB14, IGF2BP1, PLA2G6, CRTC1) were novel associations with BF%. Seven loci showed a larger effect on BF% than on BMI, suggestive of a primary association with adiposity, while five loci showed larger effects on BMI than on BF%, suggesting association with both fat and lean mass. In particular, the loci more strongly associated with BF% showed distinct cross-phenotype association signatures with a range of cardiometabolic traits revealing new insights in the link between adiposity and disease risk.
Conflict of interest statement
R.E. received honoraria for lectures from the following companies (within the past 2 years): MSD Sharp&Dohme and Pfizer. J.M.J. disclosed Trinity Partners, Inc., Osteoarthritis Research Society International, Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of US Bone and Joint Initiative, Samumed, Interleukin Genetics, Inc. and Algynomics, Inc. K.S. is a full-time employee of GlaxoSmithKline. D.S. received honoraria for lectures from the following companies (within the past 2 years): MSD Sharp&Dohme. E.S.-T. received honoraria for lectures, research grants and consultancy fees from the following companies (within the past 2 years): Aegerion, Fresenius, MSD Sharp&Dohme, Pfizer and Sanofi. Peter Vollenweider received an unrestricted grant from GSK to build the CoLaus study.
Figures

Figure 1. Regional plots of the four…
Figure 1. Regional plots of the four newly identified loci that reached genome-wide significant association…
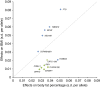
Figure 2. Comparison of effects of the…
Figure 2. Comparison of effects of the 12 loci on body fat percentage ( x …

Figure 3. Genotype influences Pol2 binding at…
Figure 3. Genotype influences Pol2 binding at rs4808844.
( a ) UCSC Genome browser track…
References
-
- Chambers J. C. et al. Common genetic variation near MC4R is associated with waist circumference and insulin resistance. Nat. Genet. 40, 716–718 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MR/K002414/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A100_1003/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK106236/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/J012165/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK075787/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR041398/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- IK2 CX000729/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089256/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U147574242/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 19167/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- K01 HL129892/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/J010642/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179472/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- U24 AG051129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K013351/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 281641/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- K01 AR062655/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K006584/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- R01 HL117078/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_A620_1016/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 10589/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

