4Pi-RESOLFT nanoscopy
- PMID: 26833381
- PMCID: PMC4740410
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10504
4Pi-RESOLFT nanoscopy
Abstract
By enlarging the aperture along the optic axis, the coherent utilization of opposing objective lenses (4Pi arrangement) has the potential to offer the sharpest and most light-efficient point-spread-functions in three-dimensional (3D) far-field fluorescence nanoscopy. However, to obtain unambiguous images, the signal has to be discriminated against contributions from lobes above and below the focal plane, which has tentatively limited 4Pi arrangements to imaging samples with controllable optical conditions. Here we apply the 4Pi scheme to RESOLFT nanoscopy using two-photon absorption for the on-switching of fluorescent proteins. We show that in this combination, the lobes are so low that low-light level, 3D nanoscale imaging of living cells becomes possible. Our method thus offers robust access to densely packed, axially extended cellular regions that have been notoriously difficult to super-resolve. Our approach also entails a fluorescence read-out scheme that translates molecular sensitivity to local off-switching rates into improved signal-to-noise ratio and resolution.
Figures

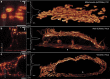
 collected from an xz-section through an actin fibre bundle (struct.) in a cell expressing Lifeact-Dronpa-M159T. Target resolution 50 nm, read-out pattern hro with a total power of Pro=3.1 μW incident on the sample. An n-component multi-exponential fit to the data corresponds to n apparent switching speeds
collected from an xz-section through an actin fibre bundle (struct.) in a cell expressing Lifeact-Dronpa-M159T. Target resolution 50 nm, read-out pattern hro with a total power of Pro=3.1 μW incident on the sample. An n-component multi-exponential fit to the data corresponds to n apparent switching speeds  . A minimum of n=3 is required to adequately represent the data from the beginning of the read-out pulse t=0 up to 0.5 ms,
. A minimum of n=3 is required to adequately represent the data from the beginning of the read-out pulse t=0 up to 0.5 ms,  (for up to 2.5 ms: n=4,
(for up to 2.5 ms: n=4,  ). Images Σ0,1,3 integrated over time regimes that are dominated by fast (hfast), slow (hslow) and about constant PSF components (hconst) exhibit a declining resolution. (d) Rate-gated 4Pi-RESOLFT. Extrapolation of the initial contribution of hslow (=S0), based on integrated images Σ1 (≈S1) and Σ2 (≈S2), t0=40 μs, provides an estimate of the partial image generated by hfast (F0≈ Σ0−S0, inset), improving resolution and image fidelity over Σ0. Details are provided in Methods. (e) Rate-gated xz-sections through actin fibres, recorded with open pinhole to boost out-of-focus signal. The measured (y-integrated) side-lobe structure closely resembles the numerical prediction and can be further suppressed (right) by an additional z-donut hzd (overlay, Ezd=1.8 μW·1.0 ms). Simulation parameters, numerical aperture 1.20, refractive index 1.362, pinhole diameter 0.5 airy units (e: open pinhole). Pulse parameters, Eac, E3d, Ero=1.6 mW·0.2 ms, 1.3 μW·1.6 ms, 3.1 μW·2.5 ms (e: 0.5 ms). Scale bars, 250 nm.
). Images Σ0,1,3 integrated over time regimes that are dominated by fast (hfast), slow (hslow) and about constant PSF components (hconst) exhibit a declining resolution. (d) Rate-gated 4Pi-RESOLFT. Extrapolation of the initial contribution of hslow (=S0), based on integrated images Σ1 (≈S1) and Σ2 (≈S2), t0=40 μs, provides an estimate of the partial image generated by hfast (F0≈ Σ0−S0, inset), improving resolution and image fidelity over Σ0. Details are provided in Methods. (e) Rate-gated xz-sections through actin fibres, recorded with open pinhole to boost out-of-focus signal. The measured (y-integrated) side-lobe structure closely resembles the numerical prediction and can be further suppressed (right) by an additional z-donut hzd (overlay, Ezd=1.8 μW·1.0 ms). Simulation parameters, numerical aperture 1.20, refractive index 1.362, pinhole diameter 0.5 airy units (e: open pinhole). Pulse parameters, Eac, E3d, Ero=1.6 mW·0.2 ms, 1.3 μW·1.6 ms, 3.1 μW·2.5 ms (e: 0.5 ms). Scale bars, 250 nm.
References
-
- Hell S. W. Double-confocal scanning microscope. European Patent 0491289. (1992).
-
- Hell S. W. & Stelzer E. H. K. Properties of a 4pi confocal fluorescence microscope. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 9, 2159–2166 (1992).
-
- Gustafsson M. G. L., Agard D. A. & Sedat J. W. Sevenfold improvement of axial resolution in 3D widefield microscopy using two objective lenses. Proc. Soc. Photo-Opt. Instrum. Eng. 2412, 147–156 (1995).
-
- Eggeling C., Willig K. I., Sahl S. J. & Hell S. W. Lens-based fluorescence nanoscopy. Q. Rev. Biophys. 48, 178–243 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Schmidt R. et al. Spherical nanosized focal spot unravels the interior of cells. Nat. Methods 5, 539–544 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

