Advances in pathogenesis and treatment of systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 26833515
- PMCID: PMC4954332
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.16-1-55
Advances in pathogenesis and treatment of systemic sclerosis
Abstract
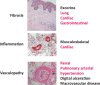
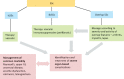
Systemic sclerosis is the most severe disease within the scleroderma spectrum and is a major medical challenge with high mortality and morbidity. There have been advances in understanding of pathogenesis that reflect the interplay between immune-inflammatory processes and vasculopathy and fibrosis. It can be regarded as a disease of connective tissue repair and this leads to organ-based complications. However the aetiology and triggering events remain to be elucidated. Treatment is available for many aspects of the disease although the available therapies are not curative and some complications remain very challenging, especially non-lethal manifestations such as fatigue, calcinosis and anorectal dysfunction. Immunosuppression is now established as a beneficial approach but balancing risk and benefit is vital, especially for powerful approaches such as autologous stem cell transplantation.
Keywords: Scleroderma; autoantibodies; fibrosis; pulmonary hypertension; systemic sclerosis.
© Royal College of Physicians 2016. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Nihtyanova SI, Tang EC, Coghlan JG. et al. Improved survival in systemic sclerosis is associated with better ascertainment of internal organ disease: a retrospective cohort study. QJM 2010;103:109–15. - PubMed
-
- Martín JE, Bossini-Castillo L, Martín J. Unraveling the genetic component of systemic sclerosis. Hum Genet 2012;131:1023–37. - PubMed
-
- Fonseca C, Lindahl GE, Ponticos M, et al. A polymorphism in the CTGF promoter region associated with systemic sclerosis. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1210–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

