Insulin-like growth factor 1 has multisystem effects on foetal and preterm infant development
- PMID: 26833743
- PMCID: PMC5069563
- DOI: 10.1111/apa.13350
Insulin-like growth factor 1 has multisystem effects on foetal and preterm infant development
Abstract
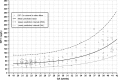
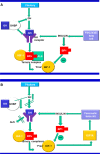
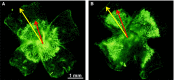
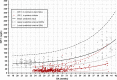
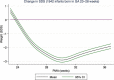
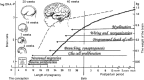
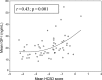
Poor postnatal growth after preterm birth does not match the normal rapid growth in utero and is associated with preterm morbidities. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) axis is the major hormonal mediator of growth in utero, and levels of IGF-1 are often very low after preterm birth. We reviewed the role of IGF-1 in foetal development and the corresponding preterm perinatal period to highlight the potential clinical importance of IGF-1 deficiency in preterm morbidities.
Conclusion: There is a rationale for clinical trials to evaluate the potential benefits of IGF-1 replacement in very preterm infants.
Keywords: Development; Foetus; Insulin-like growth factor 1; Metabolism; Preterm infant.
©2016 The Authors. Acta Paediatrica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Foundation Acta Paediatrica.
Figures
References
-
- Han VK, D'Ercole AJ, Lund PK. Cellular localization of somatomedin (insulin‐like growth factor) messenger RNA in the human fetus. Science 1987; 236: 193–7. - PubMed
-
- Schwander JC, Hauri C, Zapf J, Froesch ER. Synthesis and secretion of insulin‐like growth factor and its binding protein by the perfused rat liver: dependence on growth hormone status. Endocrinology 1983; 113: 297–305. - PubMed
-
- Blakesley VA, Scrimgeour A, Esposito D, Le Roith D. Signaling via the insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor: does it differ from insulin receptor signaling? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 1996; 7: 153–9. - PubMed
-
- Bondy CA, Werner H, Roberts CT Jr, LeRoith D. Cellular pattern of insulin‐like growth factor‐I (IGF‐I) and type I IGF receptor gene expression in early organogenesis: comparison with IGF‐II gene expression. Mol Endocrinol 1990; 4: 1386–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

