Cost-Effectiveness of Comprehensive, Integrated Care for First Episode Psychosis in the NIMH RAISE Early Treatment Program
- PMID: 26834024
- PMCID: PMC4903057
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbv224
Cost-Effectiveness of Comprehensive, Integrated Care for First Episode Psychosis in the NIMH RAISE Early Treatment Program
Abstract
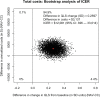
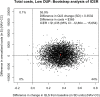
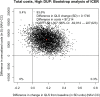
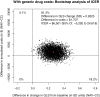
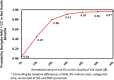
This study compares the cost-effectiveness of Navigate (NAV), a comprehensive, multidisciplinary, team-based treatment approach for first episode psychosis (FEP) and usual Community Care (CC) in a cluster randomization trial. Patients at 34 community treatment clinics were randomly assigned to either NAV (N = 223) or CC (N = 181) for 2 years. Effectiveness was measured as a one standard deviation change on the Quality of Life Scale (QLS-SD). Incremental cost effectiveness ratios were evaluated with bootstrap distributions. The Net Health Benefits Approach was used to evaluate the probability that the value of NAV benefits exceeded its costs relative to CC from the perspective of the health care system. The NAV group improved significantly more on the QLS and had higher outpatient mental health and antipsychotic medication costs. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was $12 081/QLS-SD, with a .94 probability that NAV was more cost-effective than CC at $40 000/QLS-SD. When converted to monetized Quality Adjusted Life Years, NAV benefits exceeded costs, especially at future generic drug prices.
Keywords: cost-effectiveness; quality adjusted life years; schizophrenia.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center 2016.
Figures


References
-
- McGorry P, Johanessen JO, Lewis S, et al. Early intervention in psychosis: keeping faith with evidence-based health care. Psychol Med. 2010;40:399–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

