Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation of intranasally administered liposomal formulation of donepezil
- PMID: 26834457
- PMCID: PMC4716722
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S93937
Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation of intranasally administered liposomal formulation of donepezil
Abstract
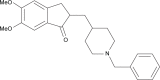
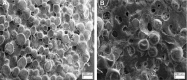
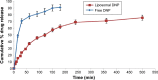
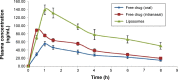
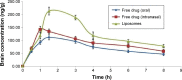
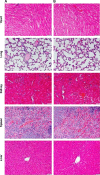
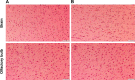
The adequate amount of drug delivery to the brain in neurological patients is a major problem faced by the physicians. Recent studies suggested that intranasal administration of liposomal formulation may improve the drug delivery to the brain. In the present study, an attempt was made to study the brain bioavailability of commonly used anti-Alzheimer drug donepezil (DNP) liposomal formulation by intranasal route in rats. We adopted the thin layer hydration technique for the preparation of liposomes by using cholesterol, polyethylene glycol, and 1,2-distearyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DSPC). The prepared liposomes were characterized by determining particle size, shape, surface morphology, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, and in vitro release of DNP. The pharmacokinetic parameters of liposomal DNP in plasma and brain of rats were determined following oral and nasal administration. The results of this study showed that the DNP liposomal formulation was stable with a consistent size (102 ± 3.3 nm) and shape. The prepared liposomes showed high encapsulation efficiency (84.91% ±3 .31%) and sustained-release behavior. The bioavailability of DNP in plasma and brain increased significantly (P<0.05) after administration of liposomal formulation by the intranasal route. Histopathological examination showed that the formulation was safe and free from toxicity. It can be concluded that the nasal administration of liposomal preparation may provide an efficient and reliable mode of drug delivery to the central nervous system.
Keywords: bioavailability; blood–brain barrier; donepezil; intranasal; liposomes.
Figures
References
-
- Matsumoto J, Takata F, Machida T, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α-stimulated brain pericytes possess a unique cytokine and chemokine release profile and enhance microglial activation. Neurosci Lett. 2014;578:133–138. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Garcia E, Andrieux K, Gil S, Couvreur P. Colloidal carriers and blood-brain barrier (BBB) translocation: a way to deliver drugs to the brain? Int J Pharm. 2005;298(2):274–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

