Relative Power of Specific EEG Bands and Their Ratios during Neurofeedback Training in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
- PMID: 26834615
- PMCID: PMC4712412
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00723
Relative Power of Specific EEG Bands and Their Ratios during Neurofeedback Training in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
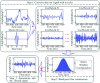
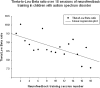
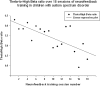
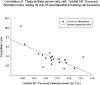
Neurofeedback is a mode of treatment that is potentially useful for improving self-regulation skills in persons with autism spectrum disorder. We proposed that operant conditioning of EEG in neurofeedback mode can be accompanied by changes in the relative power of EEG bands. However, the details on the change of the relative power of EEG bands during neurofeedback training course in autism are not yet well explored. In this study, we analyzed the EEG recordings of children diagnosed with autism and enrolled in a prefrontal neurofeedback treatment course. The protocol used in this training was aimed at increasing the ability to focus attention, and the procedure represented the wide band EEG amplitude suppression training along with upregulation of the relative power of gamma activity. Quantitative EEG analysis was completed for each session of neurofeedback using wavelet transform to determine the relative power of gamma and theta/beta ratio, and further to detect the statistical changes within and between sessions. We found a linear decrease of theta/beta ratio and a liner increase of relative power of gamma activity over 18 weekly sessions of neurofeedback in 18 high functioning children with autism. The study indicates that neurofeedback is an effective method for altering EEG characteristics associated with the autism spectrum disorder. Also, it provides information about specific changes of EEG activities and details the correlation between changes of EEG and neurofeedback indexes during the course of neurofeedback. This pilot study contributes to the development of more effective approaches to EEG data analysis during prefrontal neurofeedback training in autism.
Keywords: EEG bands' ratios; autism spectrum disorder; electroencephalography; gamma activity; neurofeedback.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Neurofeedback training aimed to improve focused attention and alertness in children with ADHD: a study of relative power of EEG rhythms using custom-made software application.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2013 Jul;44(3):193-202. doi: 10.1177/1550059412458262. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23820311
-
Frontal brain activity and cognitive processing speed in multiple sclerosis: An exploration of EEG neurofeedback training.Neuroimage Clin. 2019;22:101716. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101716. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Neuroimage Clin. 2019. PMID: 30798167 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neurofeedback Effects on Evoked and Induced EEG Gamma Band Reactivity to Drug-related Cues in Cocaine Addiction.J Neurother. 2010 Jul;14(3):195-216. doi: 10.1080/10874208.2010.501498. J Neurother. 2010. PMID: 20976131 Free PMC article.
-
Resting-state EEG power differences in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Dec 14;13(1):389. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02681-2. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38097538 Free PMC article.
-
Preventing relapse in alcohol disorder with EEG-neurofeedback as a neuromodulation technique: A review and new insights regarding its application.Addict Behav. 2020 Jul;106:106391. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106391. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Addict Behav. 2020. PMID: 32197211 Review.
Cited by
-
A bibliometric analysis of global research status and trends in neuromodulation techniques in the treatment of autism spectrum disorder.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Mar 20;23(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-04666-3. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36941549 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological Frequency Band Ratio Measures Conflate Periodic and Aperiodic Neural Activity.eNeuro. 2020 Dec 22;7(6):ENEURO.0192-20.2020. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0192-20.2020. Print 2020 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2020. PMID: 32978216 Free PMC article.
-
An Exploratory Study of Training Intensity in EEG Neurofeedback.Neural Plast. 2021 Mar 11;2021:8881059. doi: 10.1155/2021/8881059. eCollection 2021. Neural Plast. 2021. PMID: 33777137 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted Brain Network in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 24;7(1):16253. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16440-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29176705 Free PMC article.
-
Simplified Attachable EEG Revealed Child Development Dependent Neurofeedback Brain Acute Activities in Comparison with Visual Numerical Discrimination Task and Resting.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 23;22(19):7207. doi: 10.3390/s22197207. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36236305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aman M. G., Singh N. N. (1994). Aberrant Behavior Checklist—Community. Supplementary Manual. East Aurora, NY: Slosson Educational Publications.
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2000). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Edn. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing.
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edn. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

