International publication trends and collaboration performance of China in healthcare science and services research
- PMID: 26834970
- PMCID: PMC4733273
- DOI: 10.1186/s13584-016-0061-z
International publication trends and collaboration performance of China in healthcare science and services research
Abstract
Background: In recent years, China's healthcare reforms and related studies have drawn particular global attention. The main objective of this study is to evaluate quantitatively the publication trends and collaboration performance of China in healthcare science and services (HSS) research.
Methods: Scientometric methods and visualization technology were used to survey the growth and development trends of HSS research based on the Web of Science publications during the past 15 years.
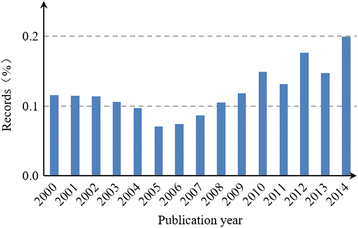
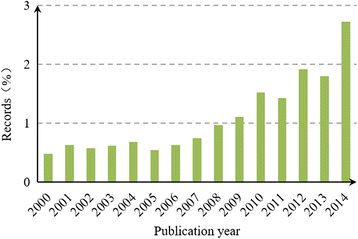
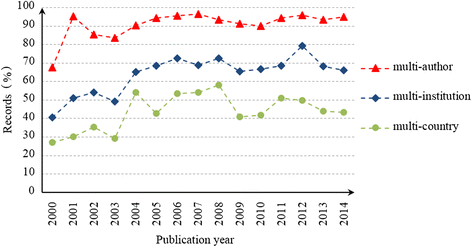
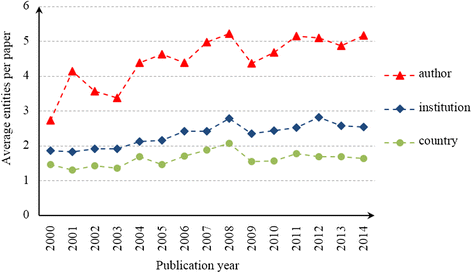
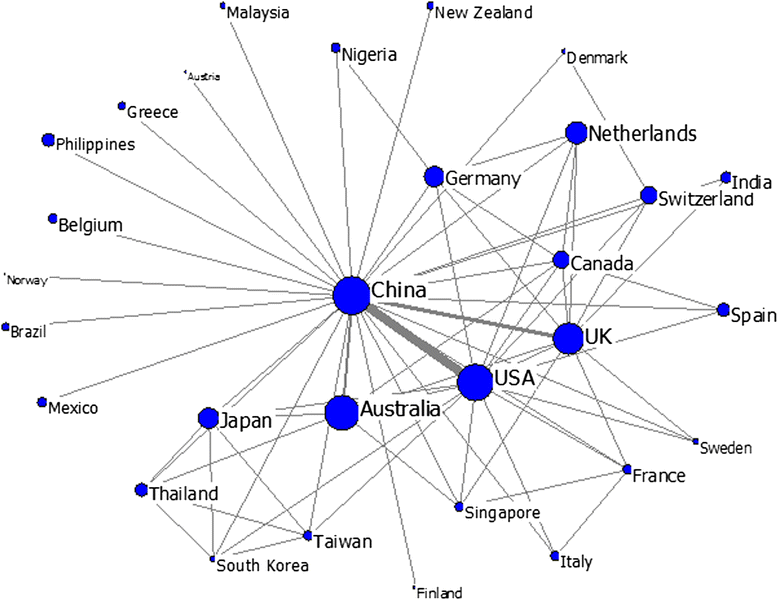
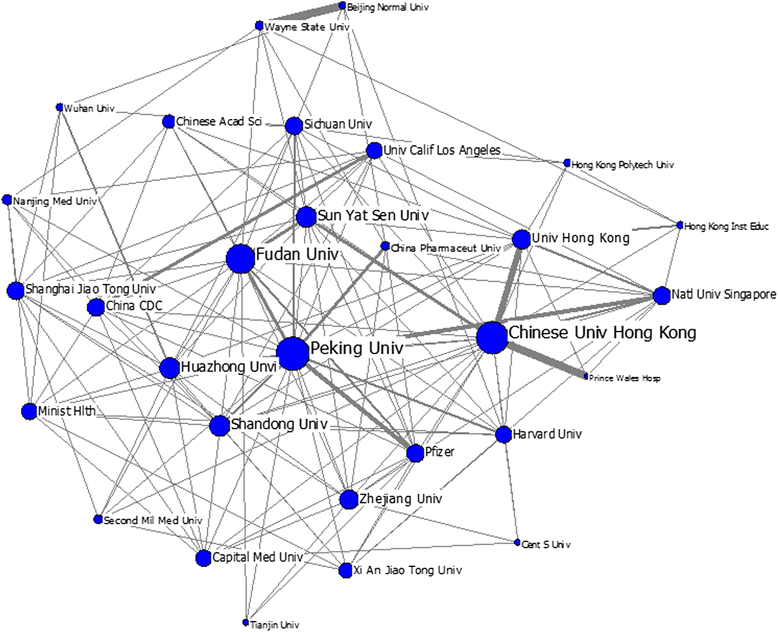
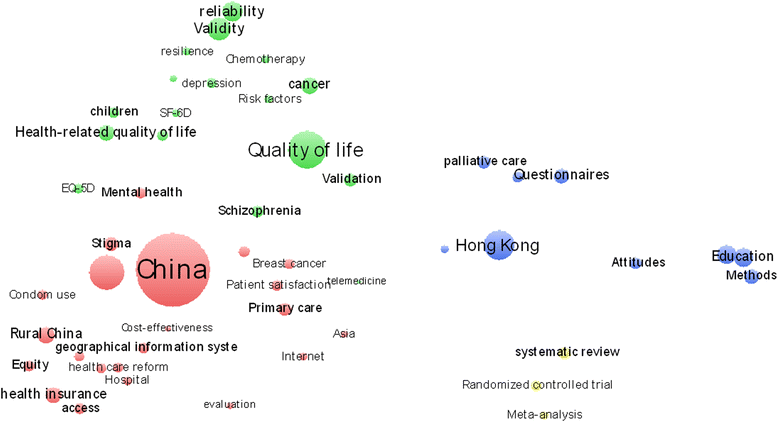
Results: China's international publications on HSS research increased rapidly compared to those of the global HSS and Chinese scientific studies. Growth trends indicate that collaboration among countries, institutions and authors has also increased. China's leading partners were all developed countries, such as the US, the UK, Australia and Canada, which have contributed to the majority of the joint publications. The academic impact of publications involving partners from European and American countries was relatively higher than those involving partners from Asian countries. Prominent institutions were universities that could be primarily classified into two groups, namely, Mainland China on the one hand and Hong Kong universities and foreign universities on the other. The most prominent actors were elite institutions, such as Peking University, Fudan University, Chinese University of Hong Kong, University of Hong Kong. The papers published by the Chinese Ministry of Health had relatively high academic impact, whereas those published by Mainland China universities alone had a lower academic impact compared to foreign cooperation papers. Issues related to the Chinese healthcare reform, priority diseases (e.g., breast cancer, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, etc.), health systems performance, quality of life and measurement tools, aging problems and research methods have been the most popular HSS topics in China in recent years.
Conclusions: Despite the extensive achievement of the Chinese HSS reforms and research, gaps and challenges remain to be addressed, including those related to health insurance and the effects of the evaluation of essential medicine systems, human resources training and allocation in the health sector, government hospitals reforms and health services systems remodeling. These findings could help scholars and decision-makers understand the current status and likely future trends of the Chinese HSS research, and help them select the most appropriate collaboration partners and policies.
Keywords: China; Collaboration patterns; Healthcare science and services; Publication trends; Research topics; Web of Science.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing the evolution of scientific publications in orthopedics journals from mainland China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan: a 12-year survey of the literature.J Orthop Surg Res. 2016 Jun 17;11(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13018-016-0404-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27317092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bibliometric analysis of international publications and citation trends of articles in mental health produced by Chinese institutions in mainland China (1990-2019).Glob Ment Health (Camb). 2021 Sep 28;8:e37. doi: 10.1017/gmh.2021.35. eCollection 2021. Glob Ment Health (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34631113 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the outcomes of medical informatics development as a discipline in China: A publication perspective.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018 Oct;164:75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018. PMID: 30195433
-
Scientific publications in anesthesiology journals from mainland China, Taiwan, and Hong Kong: a 10-year survey of the literature.Anesth Analg. 2010 Mar 1;110(3):918-21. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181c793ee. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Anesth Analg. 2010. PMID: 19955511
-
China's Contribution to Anesthesiology Research: A 10-Year Survey of the Literature.Anesth Analg. 2016 May;122(5):1640-5. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001225. Anesth Analg. 2016. PMID: 27003916 Review.
Cited by
-
Global research mapping of substance use disorder and treatment 1971-2017: implications for priority setting.Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2019 May 17;14(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13011-019-0204-7. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2019. PMID: 31101059 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in global health research among universities in China: a bibliometric analysis.Glob Health Res Policy. 2023 Apr 6;8(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s41256-023-00295-1. Glob Health Res Policy. 2023. PMID: 37024983 Free PMC article.
-
International scientific communications in the field of colorectal tumour markers.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2017 May 27;9(5):127-138. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v9.i5.127. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2017. PMID: 28603585 Free PMC article.
-
Head and neck cancer research collaborations between the United States and low- and middle-income countries: 10-year publication analysis.Head Neck. 2021 Aug;43(8):2395-2404. doi: 10.1002/hed.26703. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Head Neck. 2021. PMID: 33818838 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza vaccine hesitancy and its determinants among Lebanese public transportation drivers.Vaccine X. 2024 Dec 25;22:100606. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2024.100606. eCollection 2025 Jan. Vaccine X. 2024. PMID: 39845631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of People’s Republic of China . China Health Statistics Yearbook 2013. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press; 2013.
-
- Li L, Chen Q, Powers D. Chinese healthcare reform a shift toward social development. Mod Chin. 2012;38:630–45. doi: 10.1177/0097700412457913. - DOI
-
- Around the “Chinese medical reform” of ups and downs in the six inflection point. Oe Weekly (Focus) 2009:20–23.
-
- Inventory of Chinese medical reform 30 years (1980–2013). J Med Inform. 2013;34:96.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

