Mechanisms of Heart Block after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement - Cardiac Anatomy, Clinical Predictors and Mechanical Factors that Contribute to Permanent Pacemaker Implantation
- PMID: 26835105
- PMCID: PMC4711557
- DOI: 10.15420/aer.2015.04.02.81
Mechanisms of Heart Block after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement - Cardiac Anatomy, Clinical Predictors and Mechanical Factors that Contribute to Permanent Pacemaker Implantation
Abstract
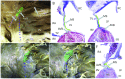
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) has emerged as a valuable, minimally invasive treatment option in patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis at prohibitive or increased risk for conventional surgical replacement. Consequently, patients undergoing TAVR are prone to peri-procedural complications including cardiac conduction disturbances, which is the focus of this review. Atrioventricular conduction disturbances and arrhythmias before, during or after TAVR remain a matter of concern for this high-risk group of patients, as they have important consequences on hospital duration, short- and long-term medical management and finally on decisions of device-based treatment strategies (pacemaker or defibrillator implantation). We discuss the mechanisms of atrioventricular disturbances and characterise predisposing factors. Using validated clinical predictors, we discuss strategies to minimise the likelihood of creating permanent high-grade heart block, and identify factors to expedite the decision to implant a permanent pacemaker when the latter is unavoidable. We also discuss optimal pacing strategies to mitigate the possibility of pacing-induced cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: TAVR; aortic stenosis; atrioventricular block; permanent pacemaker.
Figures
References
-
- Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack M et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1597–607. - PubMed
-
- Baan J Jr, Yong ZY, Koch KT et al. Factors associated with cardiac conduction disorders and permanent pacemaker implantation after percutaneous aortic valve implantation with the CoreValve prosthesis. Am Heart J. 2010;159:497–503. - PubMed
-
- Siontis GC, Jüni P, Pilgrim T et al. Predictors of permanent pacemaker implantation in patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing TAVR: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:129–40. - PubMed
-
- Kawashima T, Sato F. Visualising anatomical evidences on atrioventricular conduction system for TAVI. Int J Cardiol. 2014;174:1–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources