Endoscopic craniosynostosis repair
- PMID: 26835342
- PMCID: PMC4729850
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2224-4336.2014.07.03
Endoscopic craniosynostosis repair
Abstract
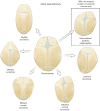
Introduction: Craniosynostosis is a rare condition that affects approximately one child in every 2,000 live births, and involves pathological fusion of two or more skull bones. Consequences of craniosynostosis include possible limitation of brain growth and cosmetic effects on the appearance of the child. Traditional repairs for these conditions over the past 3-4 decades have involved an open operation with a large skin incision and major manipulations of the skull bones. More recently, minimally invasive endoscopic techniques have been developed to release the skull bones, followed by postoperative treatment with either an external orthosis or internal springs and distractors to achieve the desired correction.
Methods: In this review minimally invasive endoscopic repair will be reviewed. A general overview of the condition and techniques for correction will be discussed, followed by specific application of these surgeries for different craniosynostosis diagnoses. Attention to the subtleties of each specific condition will be highlighted.
Summary: Over the past two decades clinical experience and a large number of publications have substantiated the benefits of minimally invasive endoscopic techniques for the treatment of craniosynostosis. These techniques have clear benefits for selected patients, and should be part of the standard of care for this condition at craniofacial centers.
Keywords: Craniosynostosis; endoscopic; plagiocephaly.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Clayman MA, Murad GJ, Steele MH, et al. History of craniosynostosis surgery and the evolution of minimally invasive endoscopic techniques: the University of Florida experience. Ann Plast Surg 2007;58:285-7. - PubMed
-
- Kaufman BA, Muszynski CA, Matthews A, et al. The circle of sagittal synostosis surgery. Semin Pediatr Neurol 2004;11:243-8. - PubMed
-
- Mehta VA, Bettegowda C, Jallo GI, et al. The evolution of surgical management for craniosynostosis. Neurosurg Focus 2010;29:E5. - PubMed
-
- Barone CM, Jimenez DF. Endoscopic craniectomy for early correction of craniosynostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 1999;104:1965-73; discussion 1974-5. - PubMed
-
- Jimenez DF, Barone CM, Cartwright CC, et al. Early management of craniosynostosis using endoscopic-assisted strip craniectomies and cranial orthotic molding therapy. Pediatrics 2002;110:97-104. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
