The Influence of C-Ions and X-rays on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 26835420
- PMCID: PMC4718996
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00005
The Influence of C-Ions and X-rays on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Abstract
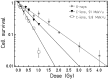
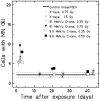
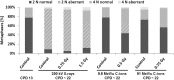
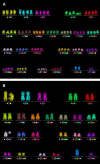
Damage to the endothelium of blood vessels, which may occur during radiotherapy, is discussed as a potential precursor to the development of cardiovascular disease. We thus chose human umbilical vein endothelial cells as a model system to examine the effect of low- and high-linear energy transfer (LET) radiation. Cells were exposed to 250 kV X-rays or carbon ions (C-ions) with the energies of either 9.8 MeV/u (LET = 170 keV/μm) or 91 MeV/u (LET = 28 keV/μm). Subculture of cells was performed regularly up to 46 days (~22 population doublings) post-irradiation. Immediately after exposure, cells were seeded for the colony forming assay. Additionally, at regular intervals, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) (JC-1 staining) and cellular senescence (senescence-associated β-galactosidase staining) were assessed. Cytogenetic damage was investigated by the micronucleus assay and the high-resolution multiplex fluorescence in situ hybridization (mFISH) technique. Analysis of radiation-induced damage shortly after exposure showed that C-ions are more effective than X-rays with respect to cell inactivation or the induction of cytogenetic damage (micronucleus assay) as observed in other cell systems. For 9.8 and 91 MeV/u C-ions, relative biological effectiveness values of 2.4 and 1.5 were obtained for cell inactivation. At the subsequent time points, the number of micronucleated cells decreased to the control level. Analysis of chromosomal damage by mFISH technique revealed aberrations frequently involving chromosome 13 irrespective of dose or radiation quality. Disruption of the MMP was seen only a few days after exposure to X-rays or C-ions. Cellular senescence was not altered by radiation at any time point investigated. Altogether, our data indicate that shortly after exposure C-ions were more effective in damaging endothelial cells than X-rays. However, late damage to endothelial cells was not found for the applied conditions and endpoints.
Keywords: carbon ion therapy; carbon ions; cardiovascular disease; chromosome 13; endothelial cells; high-LET radiation; micronucleus formation; senescence-associated β-galactosidase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Complex exchanges are responsible for the increased effectiveness of C-ions compared to X-rays at the first post-irradiation mitosis.Mutat Res. 2010 Aug 14;701(1):52-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2010.03.004. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 20298802
-
Induction of reproductive cell death and chromosome aberrations in radioresistant tumour cells by carbon ions.Int J Radiat Biol. 2004 Jun;80(6):423-35. doi: 10.1080/09553000410001702319. Int J Radiat Biol. 2004. PMID: 15362695
-
Comparable Senescence Induction in Three-dimensional Human Cartilage Model by Exposure to Therapeutic Doses of X-rays or C-ions.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016 May 1;95(1):139-146. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.02.014. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016. PMID: 27084635
-
mBAND analysis for high- and low-LET radiation-induced chromosome aberrations: a review.Mutat Res. 2011 Jun 3;711(1-2):187-92. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.12.018. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Mutat Res. 2011. PMID: 21232544 Review.
-
Review of relative biological effectiveness dependence on linear energy transfer for low-LET radiations.J Radiol Prot. 2009 Mar;29(1):5-21. doi: 10.1088/0952-4746/29/1/R01. Epub 2009 Feb 18. J Radiol Prot. 2009. PMID: 19225189 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiation-Induced Chromosomal Aberrations and Immunotherapy: Micronuclei, Cytosolic DNA, and Interferon-Production Pathway.Front Oncol. 2018 May 29;8:192. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00192. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29911071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The importance of the vascular endothelial barrier in the immune-inflammatory response induced by radiotherapy.Br J Radiol. 2018 Sep;91(1089):20170762. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20170762. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Br J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29630386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Impact of Single-Dose Fe Ion and X-Ray Irradiation on Endothelial Cell Transcriptomic and Proteomic Responses.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 22;8:570. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00570. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28993729 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-Induced Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms and Importance of Linear Energy Transfer.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Jan 31;5:5. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00005. eCollection 2018. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 29445728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship of micronucleus frequency and nuclear division index with coronary artery disease SYNTAX and Gensini scores.Anatol J Cardiol. 2017 Jun;17(6):483-489. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2017.7582. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Anatol J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28315571 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

