Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy
- PMID: 26835456
- PMCID: PMC4717291
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2015.00071
Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy
Abstract
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in women worldwide. Its surgical approach has become less and less mutilating in the last decades. However, the overall number of breast reconstructions has significantly increased lately. Nowadays, breast reconstruction should be individualized at its best, first of all taking into consideration not only the oncological aspects of the tumor, neo-/adjuvant treatment, and genetic predisposition, but also its timing (immediate versus delayed breast reconstruction), as well as the patient's condition and wish. This article gives an overview over the various possibilities of breast reconstruction, including implant- and expander-based reconstruction, flap-based reconstruction (vascularized autologous tissue), the combination of implant and flap, reconstruction using non-vascularized autologous fat, as well as refinement surgery after breast reconstruction.
Keywords: DIEP flap; autologous fat grafting; breast cancer; breast implants; breast reconstruction; mastectomy.
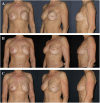
Figures

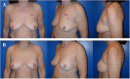

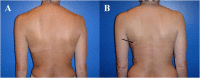
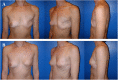
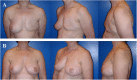
Similar articles
-
Conservative mastectomies and Immediate-DElayed AutoLogous (IDEAL) breast reconstruction: the DIEP flap.Gland Surg. 2016 Feb;5(1):24-31. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2015.05.15. Gland Surg. 2016. PMID: 26855905 Free PMC article.
-
DIEP flap with implant: a further option in optimising breast reconstruction.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009 Sep;62(9):1118-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2007.12.089. Epub 2008 Jul 9. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009. PMID: 18617454
-
Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry?Breast J. 2016 Jan-Feb;22(1):75-82. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12515. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Breast J. 2016. PMID: 26534828 Clinical Trial.
-
Trends in tertiary breast reconstruction: literature review and single centre experience.Breast. 2013 Apr;22(2):173-178. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2012.06.004. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Breast. 2013. PMID: 22795362 Review.
-
Dynamic InfraRed Thermography (DIRT) in DIEP-flap breast reconstruction: A review of the literature.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2019 Nov;242:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2019.08.008. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2019. PMID: 31563818 Review.
Cited by
-
Utilizing NPWT improving skin graft taking in reconstruction for extended breast skin defects following mastectomy.Clin Case Rep. 2021 Oct 4;9(10):e04716. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.4716. eCollection 2021 Oct. Clin Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34631060 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Quality of Life (BREAST-Q) in Patients with Mastectomy and Breast Reconstruction.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Sep 15;18(18):9707. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18189707. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34574627 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Radiotherapy on the Sequence and Eligibility of Breast Reconstruction: Current Evidence and Controversy.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;16(17):2939. doi: 10.3390/cancers16172939. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast reconstruction and quality of life five years after cancer diagnosis: VICAN French National cohort.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jul;194(2):449-461. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06626-z. Epub 2022 May 24. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35608713
-
Treatment of Implant Exposure due to Skin Necroses after Skin Sparing Mastectomy: Initial Experiences Using a Not Selective Random Epigastric Flap.World J Surg. 2017 Oct;41(10):2559-2565. doi: 10.1007/s00268-017-4041-4. World J Surg. 2017. PMID: 28466362
References
-
- Fisher B, Bauer M, Margolese R, Poisson R, Pilch Y, Redmond C, et al. Five-year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy and segmental mastectomy with or without radiation in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med (1985) 312(11):665–73.10.1056/NEJM198503143121102 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

