Markers of HIV reservoir size and immune activation after treatment in acute HIV infection with and without raltegravir and maraviroc intensification
- PMID: 26835516
- PMCID: PMC4729387
- DOI: 10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30482-9
Markers of HIV reservoir size and immune activation after treatment in acute HIV infection with and without raltegravir and maraviroc intensification
Abstract
Background: It is unclear whether intensification of standard highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) with entry and integrase inhibitors during acute HIV infection (AHI) could yield greater benefits in reducing markers for HIV reservoir size and immune activation.
Methods: Thai patients with Fiebig I-IV AHI were prospectively enrolled and offered treatment. They were randomised 1:1 to HAART (tenofovir/emtricitabine/efavirenz, n =31) or megaHAART, a standard regimen intensified by raltegravir/maraviroc (n =31), during the first 24 weeks of therapy. Participants were monitored at weeks 0, 2, 4, 8 and 12, then every 12 weeks. Frequencies of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) carrying HIV DNA (total, integrated and 2-LTR episomes), plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations, and frequencies of activated T cells were measured. Flexible sigmoidoscopy was performed in willing participants (n =25) at baseline, weeks 24 and 96, and proviral DNA and RNA were determined.
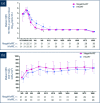
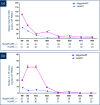
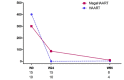
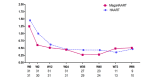
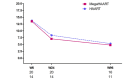
Results: Baseline characteristics were similar in the HAART and megaHAART arms. Median age was 28 years and 95% were men. Median CD4 cell count was 388 cells/mm3. HIV RNA was 5.6 log10 copies/mL. HIV RNA declined more rapidly in the first 4 weeks with megaHAART (median -3.3 log10) than HAART (-2.6 log10). Time to achieve HIV RNA <50 copies/mL was shorter with megaHAART (median 55 days) than HAART (83 days, P =0.04). Viral suppression rates after week 12 did not differ between arms, and overall, 97% achieved suppression by week 48. The frequency of cells harbouring total HIV DNA was similarly low after 96 weeks in both treatment arms (median of 7 and 4 copies/106 PBMCs in the megaHAART and HAART arms, respectively, P =0.41). At weeks 2 and 12, frequency of cells carrying 2-LTR circles were significantly higher with megaHAART (P =0.03). In the sigmoid colon, total HIV DNA and HIV RNA declined after treatment, with no differences between arms. The frequencies of cells with 2-LTR circles were also higher in the sigmoid colon at week 24 with megaHAART. Plasma levels of CRP and frequencies of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressing CD38 and HLA-DR or Ki67 were similar between arms.
Conclusions: Intensification of standard HAART with raltegravir and maraviroc was not associated with either statistically significant reductions of markers of HIV reservoir size in blood and sigmoid colon or markers of immune activation in blood.
Keywords: ART; Acute HIV infection; HIV DNA; immune activation; maraviroc; raltegravir; reservoir.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
