Performance Evaluation of Fast Microfluidic Thermal Lysis of Bacteria for Diagnostic Sample Preparation
- PMID: 26835670
- PMCID: PMC4665579
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics3010105
Performance Evaluation of Fast Microfluidic Thermal Lysis of Bacteria for Diagnostic Sample Preparation
Abstract
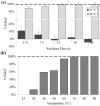
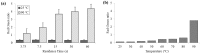
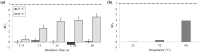
Development of new diagnostic platforms that incorporate lab-on-a-chip technologies for portable assays is driving the need for rapid, simple, low cost methods to prepare samples for downstream processing or detection. An important component of the sample preparation process is cell lysis. In this work, a simple microfluidic thermal lysis device is used to quickly release intracellular nucleic acids and proteins without the need for additional reagents or beads used in traditional chemical or mechanical methods (e.g., chaotropic salts or bead beating). On-chip lysis is demonstrated in a multi-turn serpentine microchannel with external temperature control via an attached resistive heater. Lysis was confirmed for Escherichia coli by fluorescent viability assay, release of ATP measured with bioluminescent assay, release of DNA measured by fluorometry and qPCR, as well as bacterial culture. Results comparable to standard lysis techniques were achievable at temperatures greater than 65 °C and heating durations between 1 and 60 s.
Keywords: bacterial detection; lab-on-a-chip; microfluidics; on-chip diagnostics; sample preparation; thermal lysis.
Figures


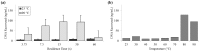

Similar articles
-
Integrated sample-to-detection chip for nucleic acid test assays.Biomed Microdevices. 2016 Jun;18(3):44. doi: 10.1007/s10544-016-0069-8. Biomed Microdevices. 2016. PMID: 27165104
-
Lysis of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria by antibacterial porous polymeric monolith formed in microfluidic biochips for sample preparation.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014 Sep;406(24):5977-87. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-8028-9. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014. PMID: 25059724
-
Microfluidic platform for rapid screening of bacterial cell lysis.J Chromatogr A. 2020 Jan 11;1610:460539. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460539. Epub 2019 Sep 10. J Chromatogr A. 2020. PMID: 31543341
-
Microfluidic sample preparation: cell lysis and nucleic acid purification.Integr Biol (Camb). 2009 Oct;1(10):574-86. doi: 10.1039/b905844c. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Integr Biol (Camb). 2009. PMID: 20023774 Review.
-
Integrated Microfluidic Nucleic Acid Isolation, Isothermal Amplification, and Amplicon Quantification.Microarrays (Basel). 2015 Oct 20;4(4):474-89. doi: 10.3390/microarrays4040474. Microarrays (Basel). 2015. PMID: 27600235 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Particle Diffusometry: An Optical Detection Method for Vibrio cholerae Presence in Environmental Water Samples.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 11;9(1):1739. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38056-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30741961 Free PMC article.
-
Paper-based molecular diagnostic for Chlamydia trachomatis.RSC Adv. 2014 Jan 1;4(80):42245-42251. doi: 10.1039/C4RA07911F. RSC Adv. 2014. PMID: 25309740 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex detection of bacteria on an integrated centrifugal disk using bead-beating lysis and loop-mediated amplification.Sci Rep. 2017 May 3;7(1):1460. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01415-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28469259 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Efficient On-Chip Photothermal Cell Lysis for Nucleic Acid Extraction Using Localized Plasmonic Heating of Strongly Absorbing Au Nanoislands.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023 Jul 26;15(29):34323-34331. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c01856. Epub 2023 Jul 12. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023. PMID: 37435756 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid point-of-care detection of BK virus in urine by an HFman probe-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay and a finger-driven microfluidic chip.PeerJ. 2023 Mar 8;11:e14943. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14943. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36915661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gubala V., Harris L.F., Ricco A.J., Tan M.X., Williams D.E. Point of care diagnostics: Status and future. Anal. Chem. 2011;84:487–515. - PubMed
-
- Yager P., Edwards T., Fu E., Helton K., Nelson K., Tam M.R., Weigl B.H. Microfluidic diagnostic technologies for global public health. Nature. 2006;442:412–418. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

